The Perm region today is an administrative-territorial division that includes 25 cities, 26 urban-type settlements (urban-type settlements) and also smaller villages, the total population of which is 2,599,260 people. At the same time, the Perm region includes a territory with a total area of 160,237 km2. Thus, the population density here today is 16.22 people / square kilometer.
But the specificity of the distribution of residents here is such that citizens predominantly populate urban areas and urban settlements, but in villages, hamlets and towns the number of residents is insignificant. If we consider these data in percentage terms, then the urban population in the Perm Territory accounts for almost 76%, which indicates an uneven distribution of people throughout the region.
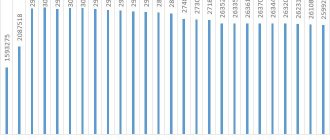
Rating of cities in the Perm region by population
Population of the Perm Territory: numbers, large cities
03/30/2021 The population of the Perm Territory as of January 1, 2021 is 2,579,261 people. The population of the Perm Territory as of January 1, 2022 is 2,599,260 people. The population of the Perm Territory as of January 1, 2015 was 2,637,032 people. According to operational data from Rosstat dated March 19, 2021, “Estimation of the resident population as of January 1, 2022 and on average for 2022.”
As of January 1, 2022
The largest city in the Perm region by population is Perm, followed by Berezniki and Solikamsk. There are only 2 cities with a population of 100 thousand or more.
Population of the region by municipalities (cities, districts, districts, etc.). Population of cities, large cities by population, people. According to operational data from Rosstat dated April 26, 2021, “The resident population of the Russian Federation by municipalities as of January 1, 2021.” Columns: 1 - “Name”, 2 - “Entire population”, 3: “incl. urban", 4 - "incl. rural."
Brief population data
World 2021
7.849 billion: China: 1,406 million, India: 1,373 million, USA: 331 million, Indonesia: 269 million.
743 million Russia 146.7 million, Germany 82.8, Turkey 80.8, France 67.3, UK 66, Italy 60.5
Source
see also
- Perm region
- Cities of Russia
| [ + ] Cities by regions of Russia | |
| Cities of the North-West (NWFD) | St. Petersburg (and its cities) • Leningrad region (historical Staraya Ladoga) • Arkhangelsk region • Vologda region • Kaliningrad region • Karelia • Komi • Murmansk region • Nenets Autonomous Okrug • Pskov region |
| Cities of the Volga region (Volga Federal District) | Bashkortostan • Volgograd region • Kalmykia • Kirov region • Mari El • Mordovia • Nizhny Novgorod region • Orenburg region • Penza region • Perm region • Samara region • Saratov region • Tatarstan • Udmurtia • Ulyanovsk region • Chuvashia |
| Cities of Southern Russia (SFD) | Sevastopol (including Inkerman) • Republic of Crimea • Adygea • Astrakhan region • Krasnodar region • Rostov region |
| Cities of the North Caucasus (NCFD) | Dagestan • Ingushetia • Kabardino-Balkaria • Karachay-Cherkessia • North Ossetia - Alania • Stavropol Territory • Chechen Republic |
| Cities of the Urals (Ural Federal District) | Kurgan region • Sverdlovsk region • Tyumen region • Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra • Chelyabinsk region • Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| Cities of Siberia (Siberian Federal District) | Altai Republic • Altai Territory • Irkutsk Region • Kemerovo Region • Krasnoyarsk Region • Novgorod Region • Novosibirsk Region • Omsk Region • Tomsk Region • Tyva • Khakassia |
| Cities of the Far East (FEFD) | Amur Region • Buryatia • Jewish Autonomous Region • Trans-Baikal Territory • Kamchatka Territory • Magadan Region • Primorsky Territory • Sakha (Yakutia) • Sakhalin Region • Khabarovsk Territory • Chukotka Autonomous Region |
| see also | Cities of the DPR, LPR, Transnistria, South Ossetia • Regions of Russia • Cities of Russia |
The largest cities in the Perm region
List of the largest cities in the region by population.
Permian
The city is the center of the Perm region. Perm was originally founded to develop copper and silver mining in the Urals. The city has a large number of parks, squares and architectural installations. Thanks to the developed industry, a large amount of money is invested in the development of Perm culture. New theaters and art galleries are opening, and numerous festivals are being held. The Perm State Circus is located in the central part of the city.
Population – 1,055,397 people (2020).
Berezniki
The first settlements on the site of the modern city were founded in the middle of the 16th century. Nowadays, the city is one of the developed centers of the Perm region, despite its small population. The basis of the economy is made up of chemical industry enterprises. Thanks to the high level of development of the city, social infrastructure is well developed in Berezniki, branches of leading universities in the Urals have been opened.
Population – 141 thousand people.
Solikamsk
In the 15th century, Vologda merchants began mining salt on the site of the modern city. Later, a working settlement appeared here, and then a large city. Production volumes grew every year, and today the city is called the salt capital of Russia. Solikamsk has a large number of architectural attractions. The most famous are the churches built in the 17th-18th centuries. Throughout the city there are memorials dedicated to the heroes of the Great Patriotic War.
Population – 93 thousand people.
Chaikovsky
The city was created in 1955. Its main purpose was to provide housing for the builders of the Votkinsk hydroelectric station. Tchaikovsky developed rapidly in the 20th century. These days there are a large number of concert halls located here. Music and choreographic festivals are also regularly held in Tchaikovsky. They are attended by creative teams not only from neighboring regions, but also from neighboring countries.
Population – 82.5 thousand people.
Kungur
The city was founded in the second half of the 17th century. Soon Kungur developed and a stone Kremlin was built. Today, there are a large number of historical museums and nature reserves located here. Ancient landforms and relict plants have been preserved in protected areas. Museums are associated with archaeological finds made on the territory of the Perm region and associated with local sites of primitive people.
Population – 65 thousand people.
Lysva
In 1785, an iron production plant was founded on the site of the modern city. In 1787, a workers' settlement was formed next to it. One of the main attractions of Lysva is the Savin Drama Theater. It is one of several professional theaters in the Perm region. Also in Lysva there are a large number of libraries with a large book collection.
Population – 61 thousand people.
Krasnokamsk
The basis of the city's economy is the Kama Pulp and Paper Mill. It was founded in 1929, at the same time Krasnokamsk appeared. In the middle of the 20th century, an oil refinery was founded in the city. One of the tourist attractions of Krasnokamsk is a pine forest with a large beach. Every year a large number of people come here on vacation.
Natural movement
Considering migration flows and population growth in the region, it is worth noting the following stages. Peak growth rates occurred in the following periods (number of people arriving per 1,000 population):
- 1975 – 7.4 people.
- 2001 – 6 people.
- 2004 – 6.3 people.
- If we talk about natural loss, here is when it was maximum:
- In 2000, for every thousand people, 6 citizens traveled to other cities or outside the country.
- In 2005, this figure was 7 people.
It is worth noting that the fluctuation figures have now decreased significantly. Deviations in both directions, both increasing and decreasing, became less significant. But still, the general trend is downward, which is due to a number of internal processes at the level of the entire country.
This can include a not very satisfactory level of medical care, small opportunities in terms of earning money and developing your own business. As well as a number of other factors that local residents assess as not very satisfactory, due to which negative population growth is formed, that is, in fact, a steady decline, although not having a global scale.
Medium-sized cities 20-100 thousand people
Solikamsk
Population 95,191 people (2016).
Chaikovsky
Population 83,056 people (2016).
Kungur
Population 66,311 people (2016).
Lysva
Population 63,083 people (2016).
Krasnokamsk
Population 53,964 people (2016).
Chusovoy
Population 45,546 people (2016).
Dobryanka
Population 33,194 people (2016).
Chernushka
Population 32,982 people (2016).
Kudymkar
Population 31,007 people (2016). Until December 1, 2005, it was the administrative center of the Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug.
Vereshchagino
Population 22,261 people (2016).
There are other meanings of this name
Population 21,143 people (2016).
Gubakha
Population 20,645 people (2016).
Content
- 1 Millionaire cities with more than 1 million people 1.1 Perm
- 2.1 Berezniki
- 3.1 Solikamsk
- 4.1 Nytva
Perm is the regional capital
The largest city in the Perm region is home to people of dozens of nationalities. According to many Perm residents, public transport has become one of the main problems of the city. Many large companies are private, so they may not provide travel benefits. Of course, an exception is made for students, schoolchildren and the elderly. The lack of a metro makes the situation worse; people often suffer crushes. The lack of budgets does not allow the situation to be resolved.
Perm is a large city in terms of area; only million-plus cities can boast of a larger size. In this regard, the lack of an established infrastructure, the improvement of which will require huge amounts of money, is added to the list of its problems. The Dzerzhinsky district is considered one of the most favorable in terms of infrastructure. There are quite a lot of municipal schools, kindergartens, and a large university here. The Kirovsky district offers children's clinics and a hospital for adults. There are also several sports schools here. In the Motovilikha district there are hospitals, clinics, preschool institutions, colleges and schools. Perm trams have become significantly more convenient, with seats for the disabled. The city's road network has a well-thought-out layout. Public transport moves easily through its territory, but there is a lack of interchanges, especially highways, that could connect the suburbs. An increase in the number of cars leads to an increase in traffic intensity. There are many jobs offered to Perm residents. There is a large branch, industrial enterprises, a machine-building plant, a metallurgy plant, and a printing factory. Even people from the scientific field can find here relevant organizations engaged in the study and development of technologies in the field of mining. The large number of universities resulted in a high percentage of educated citizens among the local population.
Berezniki is a developing city
The relatively large city shows an interesting population composition. It is dominated by elderly people. There is a regular outflow of young people; many are employed in the industrial sector. The most pressing problem for Berezniki was soil subsidence. Many people want to sell their apartments as soon as possible, but no one wants to take risks. Added to this problem is the poor state of the infrastructure. But thanks to the small number of cars, residents manage to avoid traffic jams.
No one will be surprised by the queues at kindergartens; the administration has to beg budgets from senior leaders in order to restore old schools and preschool institutions. Berezniki offers many higher education institutions. After them, the graduate will have a real opportunity to find a job. But not all specialties turn out to be relevant; however, even with an irrelevant specialty it is easier to get a job than without it. Employment is offered by small companies and firms. Harmful production, which is found everywhere in Berezniki, is compensated by the presence of gyms, health centers, and swimming pools. The city has two hospitals, which are located in different parts. Now Berezniki has received new medical equipment.