- November 17, 2019
- Regions
- Natalia Kalinichenko
The Magadan region is a region where permafrost remains, very harsh winters, and even gold, of which about 20 tons are mined per year. There is untouched nature and fast-flowing rivers, and there are nomadic tribes of reindeer herders. The region has the most beautiful mountains and one of the coldest seas in the whole world - Okhotsk, the water temperature of which does not rise above +10 °C even in the warmest time of the year.
The area of the Magadan region is not so large, but per 1 resident it accounts for as much as 3 square meters. km.
general characteristics
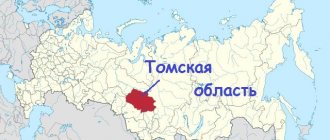
The region is the eastern region of the country and, according to its administrative-territorial division, is part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Located in the northeast of the state. It borders on the Republic of Sakha and the Khabarovsk Territory, the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The region is dominated by mountainous terrain. Plains are represented in river valleys and on the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk.
The area of the Magadan region in 2022 is 462,464 square meters. km.
The administrative district is the city of Magadan, which is considered the most comfortable in the entire Far East.
In terms of population, the region is the most sparsely populated in the entire country, while the region ranks 11th in terms of area.
Population and religion
At the beginning of this year, the population was 141,234 citizens. The majority are Russians, accounting for 80.3% of the total number. There are few indigenous people – 2.7%. The second largest nationality is Ukrainians, 9.9% of them here.
The average life expectancy in the region is 63.7 years, women live to 70.1 years, and men only to 58.1 years.
About 57% of the total population consider themselves Orthodox. Protestants are about 3.6%, and Catholics are even smaller - 2.2%.
The demographic situation has been steadily declining since the 1983s, as has the number of residents. Migration occurs mainly to the Urals, the central part of the country and the Volga region. For example, in 1987 the population of the region was 550 thousand people.
In addition to the fact that many people are leaving the region, mortality is increasing and the birth rate is decreasing. Over the past year, 1,632 people died in the region, and only 1,377 were born.
Demographics
One of the reasons for the decrease in the rate of population decline may be an increase in the birth rate. During the Soviet period, there were about 17 newborns per 1 thousand people per year. In the 90s, this figure was 8-8.5 newborns. Then a gradual, unsustainable increase began, and now the birth rate ranges from 12 to 12.5 people per thousand inhabitants per year. However, there is no data for recent years even on official websites. Most likely, the birth rate remained at the same level, since the population curve, which includes data for this year, does not show any new trends (it has a smooth course).
Mortality data also does not cover the last 4 years. Its values were minimal until 1995 (on average 5.5-6 deaths per 1000 people). Then, until 2003, it fluctuated around 9-10 people per thousand. After which the rate increased and amounted to 12.5-14 deaths per 1000 inhabitants. In 2013 and 2014, the mortality rate was slightly lower.
Natural growth was significant in the Soviet period (10.5-12.5 people/1000), slightly less in 1990 (8.1), and then mostly negative, sometimes positive, but small everywhere. Only since 2013 has it become positive, but insignificant in magnitude.
Thus, the sharp decline in the 90s is apparently associated with the migration outflow of the population to other regions of Russia, and not with the natural demographic situation in the region.
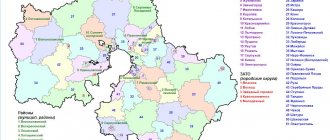
Settlements
The entire area of the Magadan region is 74 settlements, forests, lakes, rivers and endless open spaces. The largest population is in the regional center - Magadan, where 91,781 people live as of the beginning of this year. There is another city in the region - Susuman, where only 4,588 people live. The third largest settlement is the village of Ola. It has 6117 people. The population is represented predominantly by indigenous tribes. The village is located on Tauiskaya Bay, where the winds constantly blow.
The next village with a large population is the town of Sokol, with a population of 4805 people. Located literally 50 km from the capital, in the direction of Ust-Nera, in the vicinity of Magadan airport. The top five is closed by the village of Omsukchan, where 3,707 people live. It appeared in 1937 on the site of rich deposits of gold, silver, and tin.
The rest of the territory is settlements of the Magadan region, urban type and just villages. The smallest in terms of population are Taskan and Kolymskoye, where 10 people live each.
From 2014 to 2022, 11 settlements were abolished. This trend is still observed today. At the beginning of 2022, there were no longer any residents left in a number of settlements, in particular in Stan Utin, Sporny, Polevoy, Imeni Gorky, Verkhniy Art-Uryakh, Yablonevoy, Karamken, Obo and a number of others.
There are only 9 districts in the Magadan region. The largest is Olsky, consisting of 9 villages. In total, 9,637 people live in the district. The bulk of the population settled on the coast and is engaged in fishing and hunting. Hardworking residents even manage to grow potatoes and other vegetables, and this in permafrost conditions!
The smallest district is Sredne-Evansky, where only 1,938 people live on an area of 102,000 square meters. km. There are only 5 settlements in the area, whose residents are mainly engaged in the mining of gold and other precious metals and stones. There are not even roads or railways here.
Cities of the Magadan region
Magadan (95 thousand people) is a regional center founded in 1929. It was the main transshipment point connecting Bolshaya Zemlya (ports of Khabarovsk and Vladivostok) with the Kolyma mines. Today it is the main industrial center of the region, producing mechanical engineering products, primarily heavy mining equipment used in gold mines.
Magadan is also a center of fishing, food industry and science. Of course, the infrastructure here is not as developed as on the mainland. For example, high-speed Internet is only in the plans. But around the city there is beautiful northern nature, delighting the soul of every lover of hunting and fishing.
Ola is an urban-type settlement and the center of the Olsky district. Population - 6520 people. This is one of the oldest settlements in the region, founded in 1645 on the shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, at the mouth of the Ola River. During the years of Soviet power, the village developed thanks to the state farm, which supplied food to the Magadan region. And now agriculture, hunting and fishing are developed here. Despite the small population, the village has some infrastructure - it even has its own museum and theater.
Susuman is a city with a population of 5313 people, the center of the Susuman district. Translated from Even, “susuman” means “blizzard”. Indeed, the climate here is harsh, and snow storms are not uncommon. Susuman is located on the banks of the Berelekh River, at the beginning of the Kolyma Highway.
From 1949 to 1956, the administration of Zaplag, one of the largest forced labor camps, was located here. In late Soviet times, several large industrial enterprises were created in Susuman, including a mechanical repair plant, a mining and processing plant, a building materials plant, and food industry enterprises. Nowadays Susumanzoloto, the largest gold mining company in the Magadan region, is located here. But it is worth noting that gold mining in the Far North has been curtailed in recent years.
Capital
What is the federal district of Magadan? Naturally, it is Far Eastern, since the city is the administrative center of the entire region. 91,781 residents live here, that is, 64% of the total population of the region.
Where this name came from, historians have never been able to establish exactly. However, there are many versions about this. But most scientists agree that the name comes from the Even phrase “windy place”, or “mongdan”.
The capital of the Magadan region is spread over an area of 295 square meters. km. The summer here is very short with white nights but strong winds. The settlement itself is divided into two parts by the mouth of the Magadanka River. The coldest month is January, when the average air temperature is -16 °C. The warmest month of summer is August, but even at this time the temperature does not rise above +15 °C.
The architecture is represented mainly by houses built in the 50s of the last century in the neoclassical style. There are unique designs characteristic of the Stalinist Empire style.
The capital of the Magadan region received city status in 1939. The area was inhabited by gold miners. The city has a port, which is the second largest in the entire northeast of the state.
Food products in the capital are quite expensive, because it is quite problematic to deliver them here. You can get to the city by car or plane. To get to Magadan from the European part of the country by car, you will have to travel more than 10,000 km, which is at least 148 hours. The plane ride is also 7 hours. There is no railway connection, as well as passenger shipping. The port accepts exclusively cargo ships, but only from December to May.
An amazing fact: despite the severity of the climate, the city has a huge number of fountains.
Cars are almost never stolen in Magadan. And the reason is simple: there is simply nowhere to put them and no one to sell them to. In the 70s of the last century, Shufutinsky sang in a local restaurant for 3 whole years. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, a third of the population left the city within 10 years. Another interesting fact: in the capital of this region there is not a single McDonald's, but there is a local catering chain that is no worse than the American brand.
Historical information about the region
Until the 18th century, the entire area of the Magadan region was inhabited by Yukaghirs. Then the Russian Cossacks began campaigning in this region. Already in the 20-30s of the last century, geological exploration expeditions were constantly sent here. In the 1930s, the first gold mining trust opened, and the mines grew. There were many prisons in the region. Prisoners were used as free labor.
However, archaeological excavations prove that the first people appeared on these lands in the early Neolithic era.
The region received its modern borders in 1953, this year being the date of its formation. Magadan was founded in 1939 as a workers' village and became a regional center in 1954. In the same 1954, the workers' settlement received the status of a city, the name remained the same - Magadan. What region or region is this? There are nuances here. In fact, the city is the capital of the Magadan region - a subject of the Russian Federation, that is, a territorial unit.
In fact, modern legislation gives the region and the region the same legal status. Although the terms have different historical backgrounds.
In pre-revolutionary Russia, the region was a territory that had borders with other states. The region could include several regions. However, even in those days the status of the region and the region was virtually the same. Over time, the concepts became synonymous. For example, even the phrase Perm region is no longer actually used, since this region has ceased to be a border region.
Naturally, it is impossible to imagine Magadan without the Gulag camp system. In 1932, the Northeast forced labor camp appeared, which existed until 1951. In the year it was closed, there were more than 170 thousand prisoners in the camp, who, in fact, were engaged in gold mining and building the city.
Beautiful rivers, lakes and bays of the Magadan region.
Enchanting rivers and lakes delight tourists not only with clean water, rich catches and picturesque landscapes, but also with creative names.
Kolyma Reservoir
- Coordinates: 61.917417, 149.807791.
One of the largest reservoirs in the Magadan region was created artificially by Soviet engineers and builders. The reservoir was intended for the Kolyma hydroelectric power station, which began to be built near the village of Sinegorye in 1970 and put into operation in 1981.
The territory was flooded in 1980, the length of the new reservoir was 148 kilometers, the width was 6 kilometers, and the maximum depth reached an incredible 120 meters. To fill the reservoir, several important sites had to be sacrificed: water flooded six workers' villages and a valuable Paleolithic site near the Congo River.
Ola River
- Coordinates: 60.616104, 151.296281.
The Ola River is not as famous as the Kolyma, but its importance for the economy and development of the region is difficult to overestimate. A relatively small river, whose length is only 166 kilometers, generously provides residents of the region with reserves of pink salmon, chum salmon, coho salmon and other valuable fish.
Ola runs down the slopes of the Ola Plateau and flows into the Tauyskaya Bay. In the upper reaches, the river flow washes amazing agates out of the rocks and throws them onto the banks on the way to the sea.
Jack London Lake
- Coordinates: 62.076793, 149.528415.
The most famous and popular lake among tourists in the Magadan region is comfortably located among the mountain peaks of the Yagodinsky district. The reservoir is very deep, the maximum depth reaches 50 meters. The lake has an elongated shape, its length is 10 kilometers and its width is less than 2 kilometers. The natural monument is fed by the Purga River and a number of large and small streams.
The reservoir received its name in 1932 from the Soviet geologist Pyotr Skornyakov. Now it is difficult to say why the scientist chose this name.
Some believe that the discoverer was a fan of the work of the American writer Jack London, others claim that one of the prose writer’s books was found on the shore. Four small islands protrude from the water, covered with larch and dwarf cedar. On one of them, Vera Island, there is a weather station. Several years ago, the lake and its surroundings became part of the natural park of the same name.
Lake of Dancing Graylings
- Coordinates: 62.112817, 149.566297.
Near Jack London Lake there is another magnificent freshwater body of water - Lake of Dancing Graylings. This unusual name was given to the lake by foreman I. Topunov, who worked under the guidance of geologist Pyotr Skornyakov.
The reservoir is indeed rich in grayling, but there are much fewer individuals in it than in the nearby Jack London Lake. The two water brothers are connected by the Variants channel. The length of the lake is 3 kilometers, width is less than 1 kilometer. The Kuel-Sien River flows out of the reservoir.
Nagaeva Bay
- Coordinates: 59.536362, 150.598686.
Nagaev Bay is the gateway to the Sea of Okhotsk. The regional center is located on the eastern shore, and one of the largest commercial ports in the Russian North-East is located on the northern shore. During the Stalinist camps there was also a transit point for repressed people here.
The bay was named in honor of Admiral Alexei Nagaev. Unfortunately, local waters cannot be called environmentally friendly; the activities of the port and numerous ships poison the environment.
Gertner Bay
- Coordinates: 59.542839, 150.919447.
A beautiful bay on the outskirts of Tauiskaya Bay is a center of vibrant natural attractions. Gertner is adjacent to Vesyolaya Bay with the small but very colorful Vdovushka Island. Nearby you can see the island of Kekurny, on which there is a large colony of gulls.
Since 1912, the bay has been named after the famous hydrographer Konstantin Gertner. Both residents of Magadan and tourists from other cities and regions of the country come to relax on the sand and pebble beaches of the bay. All kinds of national holidays and ethnic festivals are also regularly held here.
Authorities
Depending on the type of administrative-territorial unit, authorities are formed. The question arises: the region and Magadan itself - which federal district? This entire territory is included in the Far Eastern Federal District. State power is exercised by the regional duma, headed by the governor. The local Duma is a unicameral body. This is the only legislative and supreme authority in the region.
Deputies enter the Duma through direct elections and serve for 5 years.
The structure of the executive power is determined by the governor within the scope of his competence.
Since September 2022, the post of governor has been occupied by Sergey Konstantinovich Nosov (born in 1961). This person is distinguished by excellent organizational skills and decency. He has an active political position and is a member of the United Russia party.
Before the elections to the post of governor of the Magadan region, Sergei Konstantinovich was the head of Nizhny Tagil. During his reign, he managed to bring the city to 11th position in the ranking of efficiently managed cities. During the period of Nosov’s activity, the program for the implementation of innovative improvement projects was fully implemented. New, and most importantly, affordable housing was built, lighting and landscaping work was carried out, and socially significant infrastructure facilities were repaired.
The key problem of the region, as the governor notes, is population decline. People are the fundamental factor of economic growth and prosperity. It is impossible to develop the potential of the region if there is a constant outflow of population.
At the moment, there are several programs to solve the demographic problem. There is a program to support young families, and a system of targeted assistance to low-income families. The education and health care systems are slowly but still improving, and the comfort of living in populated areas is increasing.
Those who want to move to Kolyma have the opportunity to get several hectares of Far Eastern land. There is also a proposal to return military units to the region to attract officers and their families.
Nature
Photos of the Magadan region are fascinating. The region is dominated by mountainous terrain. The harsh climate is due to the proximity of the Sea of Okhotsk. The largest peninsulas are:
- Pyangina.
- Horses.
- Tygonos.
The relief of the region is characterized by a combination of plateaus, ridges and coastal depressions.
33% of the entire territory is occupied by forests. These are mainly plants of the northern taiga type, deciduous sparse forests, where there is a lot of chosen and fragrant poplar, and rowan is found. Among the shrubs there is a lot of honeysuckle, needle rose and currant.
On the slopes in the southern part there are relict plants. In coastal areas there are fewer forests and rocky terrain predominates.
In the southwestern part of the region stretches the seismically dangerous Chersky belt. Earthquakes of magnitude 8 or higher are possible in this area.
Much of the region is covered with permafrost. On average, we are talking about 150-200 meters, and in some places the thickness of the layer reaches 400 m. On the coast, permafrost is represented by an intermittent strip.
There are 68 thousand rivers in the Magadan region. In total length they occupy 118.9 thousand km. Almost all of them are already covered with ice by the beginning of October, which disappears only by May. Most of the rivers are typical mountain rivers, with fast currents and rapids. The region is also famous for the number of lakes - there are about 25 thousand of them. This cold region of Russia is better provided with water resources than all others.
Natural conditions
The region is on the list of regions of the Far North, which in itself indicates harsh conditions. In the coastal zone, due to collisions of moist, relatively warm sea and cold continental air masses, weather disasters in the form of snow storms, drifts and other troubles can occur. On the mainland the weather is generally stable, with severe to extremely severe frosts in winter and fairly warm summers. The continental climate is clearly expressed. The frosts are about the same as in Yakutia.
Almost everywhere there is permafrost. The relief is mountainous, with a predominance of mid-altitude mountains. Earthquakes occur, with a force of up to 7-8 points.
Animal world
Despite the harsh climate, almost the entire area of the Magadan region is inhabited by many representatives of the fauna. Here you can find deer, bighorn sheep, bears, moose, squirrels and sables.
There are several reserves in the region, 11 to be exact. In particular, musk oxen, which were brought from the Taimyr Peninsula, are bred in Solnechny. In Atkinskoye they protect and protect the bighorn sheep, while Malkachansky and Kavinsky are created for migratory birds.
The waters of the Sea of Okhotsk are also rich in a variety of fish. Here, in their natural environment, coho salmon, chum and pink salmon live, and salmon spawn. In coastal waters there is a lot of pollock, scallops, shrimp, crabs, cod and sea urchins. It is in these waters that 9 species of cetacean marine representatives live. There are walruses and seals.
Mountains, rocks and islands in the Magadan region
Almost the entire territory of the Magadan region is occupied by mighty mountain ranges that hide large reserves of precious metals in their depths.
Bilibin Peak
- Coordinates: 62.193611, 149.201111.
Bilibin Peak is one of the highest and most picturesque mountains in the region and the largest peak of the Big Anngachak ridge. The height of the peak almost reaches 2300 meters. Beautiful steep cliffs on the slopes attract experienced climbers. There is snow on the top of the giant all year round, which is why the peak was previously called Snezhnaya.
The mountain was named in honor of geologist Yuri Bilibin, and the name of the famous scientist was assigned to it relatively recently - in 2003. For a long time, the peak was considered the highest point in the region, but studies in 2022 handed the palm to an unnamed mountain in the Ohandya ridge.
Aboriginal Peak
- Coordinates: 61.983954, 149.330994.
The beautiful mountain, 2286 meters high, is one of the largest peaks of the Big Anngachak ridge. The word "aboriginal" translated into Russian means "indigenous".
The peak received its Latin name in 1932 from the famous geologist Pyotr Skornyakov, who gave names to many geographical objects of the Magadan region. In 2022, the peak was declared a natural monument. The river of the same name originates on the Aborigine slope.
Hittite pillars
- Address: Kheta River.
One of the most fascinating sights in the Magadan region is the stunning rocks in the valley of the Kheta River. Stone pillars created by wind, rain and snow resemble the spiers of ancient castles. On the rocky slopes you can sometimes see coniferous trees, which seem to be trying to equal the height of the majestic rocks.
The magnificence of natural sculptures delights travelers. Remains for 15 kilometers cover Kheta from the wind with a wall. The river itself is suitable for rafting; some extreme sports enthusiasts go downstream to admire the amazing pillars.
Talan Island
- Coordinates: 59.311009, 149.082365.
On the outskirts of Tauiskaya Bay, a hundred kilometers from the regional center, a lonely island rises. An area of land with an area of 2.5 square kilometers is framed on all sides by beautiful rocks.
In summer, the island pleases the eye with lush greenery and picturesque lakes with fresh water. It is not surprising that such a delightful deserted place was chosen by a large colony of birds. During the migration period, 147 species of birds with a total number of up to 1,800,000 individuals gather on Talan.
Of all the species, only 21 nest on coastal cliffs. The noisy islanders feed on fish and small marine animals such as crustaceans and euphausids. The island is recognized as a natural monument of federal significance.
Yamskie Islands
- Coordinates: 59.329183, 155.560791.
In Shelikhov Bay, huge stone guards - stunning rock islands - appear on the way of sailors. All six giants belong to the Magadan Nature Reserve. Sparse vegetation grows here and there on the gray ledges. Many birds flock to the archipelago every year. Near the islands you can spot seals and even whales.
Zavyalov Island
- Coordinates: 59.059675, 150.628285.
The largest rocky island in the northern part of the Sea of Okhotsk has become famous as a haven for a huge colony of seabirds. About two million birds every year fill the steep walls on the island's shores, bob on the blue waves, fly screaming through the air and hunt fish in the coastal waters. The vegetation on the rocks is sparse; only a few species of flora survive in such difficult conditions.
Currently, only birds and some species of mammals live on the island, but in Soviet times it was inhabited by people who worked in an arctic fox nursery, a fish factory and a weather station.
Several years ago, the island was given the status of a natural monument, and since 2022, construction of an eco-park has been underway on it. However, the attraction attracts the attention of not only animal rights activists and ornithologists, but also historians. Eight settlements of different periods were found in different parts of the island, from the Tokarev culture of the 8th century BC to the ancient Koryak culture of the 17th century.
Resources
The Magadan region is a leader in the gold and silver mining industry. There are more than 1.2 thousand deposits in the region. Most of them are in the southwest of the region, near the Sea of Okhotsk and the Kolyma River.
Silver deposits are located mainly in the center of the region. There is a lot of hard coal in the northwest, and brown coal near the capital.
Deposits of cobalt, molybdenum, zinc, antimony, copper and other rare metals have also been discovered in the region. There are a lot of sand-gravel mixtures, expanded clay, and limestone in these depths. It was even possible to discover natural gas and oil on the sea shelf itself.
Environmental protection
About 56% of the entire territory of the region has not been touched by human hands at all. Therefore, in general, the environmental situation in the region can be called favorable. However, about 13% of the area is in a crisis situation, we are talking about Magadan, the Prikamsky region, where economic development is being actively carried out. This is due to mining, which results in complex destruction of the earth’s surface, water and air being polluted.
The most dangerous and polluting industrial facilities include the Magadan Thermal Power Plant, power plants and gold mining enterprises. The situation is also unfavorable near populated areas: rivers are polluted by household waste, resulting in increased bacterial contamination. Recently, environmentalists have noted that the amount of nutrients in drinking water has been significantly reduced.
The region is characterized by an increased level of radiation; by the way, the region is considered the most unfavorable in this regard in all of Russia. A particularly dangerous situation has developed in the Tenkinsky and Srednekamsky regions. To a greater extent, this is due to the extraction of ores with a high content of toxic elements from the bowels of the earth.
Attractiveness of the region for tourists
Almost all 462,464 sq. km - the area of the Magadan region - are a paradise for fishermen and hunters. One of the region’s attractions is the Kolyma River, which is 2,129 km long. There are many places for rafting and regular boat trips. Fishermen have a chance to catch the most unusual fish - from sockeye salmon to chum salmon.
People come here to hunt mountain sheep, bears, and deer. The potential in this regard is enormous: even annual quotas are not chosen.
There are many hot mineral springs in the area. The most popular resort is Talaya (Khasynsky district). This is a real balneological paradise, located in the cleanest part of the region at an altitude of 720 meters above sea level.
History buffs will also have plenty to do in the Magadan Territory. Here you can see real reindeer herders’ camps, communicate with real local aborigines (these are Koryaks and Evens), and hear many ancient legends.
And if you come to Magadan in July, you can visit the only “Golden Festival” in the entire country. The highlight of the festival is the "Prospector's Fortune" competition - a competition in soil panning to search for gold. The winner receives a prize of up to 1 million rubles.
There are several ski slopes in the region. However, they are more suitable for professionals, since the infrastructure is poorly developed. And of course, this is pristine nature, unique landscape and clean air.
Where the Magadan region is located is shown on the map below
Sources of the Magadan region: sacred and medicinal
It’s hard to believe, but the cold Magadan region is rich in hot springs, the waters of which have healing properties.
Motyklei springs
- Coordinates: 59.355083, 148.661667.
Thermal springs in the vicinity of the village of Balaganoe are the most popular balneological resort in the region. Based on location, springs are divided into three groups of different temperatures and degrees of mineralization:
- Pravo-Ulukansky,
- Levo-Ulukanskie,
- Middle-Ulukanskie.
The steam emanating from the hot water does not let you forget that dormant volcanoes are located nearby. In 1975, the springs were given the status of a natural monument.
Tavatum thermal springs
- Coordinates: 61.837954, 157.815479.
Thermal mineral springs near the Tavatum River are also in demand among tourists. The springs are divided into five groups, the temperature of the hottest exceeds 60°C, the temperature of the coolest is around 25°C.
The area near the springs is well-equipped, there is a children's camp, open-air swimming pools, a bathhouse, houses and a sports ground. Despite all the amenities, Tavatum springs are not as popular as some other resorts.
The reason for this is the inconvenient location and distance from populated areas. The springs flow in an amazingly beautiful valley, surrounded by low hills. In summer, the surrounding area is green with alder trees, and mushrooms and berries grow in abundance under the tree branches.
Shirokino springs
- Coordinates: 61.850290, 157.399388.
Hot springs near the river Broad is especially rich in various elements. In total, there are 38 water outlets with high mineralization. The temperature of the streams varies from 33 °C to 56 °C. Very rare plants grow near the water, such as hemp-leaved groundsel and ferruginous willowherb.
In 1975, the springs and the surrounding area were declared a natural monument. The springs are practically undeveloped, but people also come to them to improve their health with the help of medicinal baths.
Kongali Key
- Coordinates: 59.575521, 151.021106.
The narrow, unremarkable at first glance Kongali stream is one of the most interesting attractions of the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk. Travelers are drawn here not so much by the clear water of the spring, but by the opportunity to look at the stones lying near the stream.
The boulders have an unusual round shape, some compare them to dragon eggs. The path to the stream is not the shortest or easiest, but at the end of the hike tourists will be rewarded with curious creations of nature and spectacular landscapes.
Precautionary measures
However, you should be careful when traveling in the area. The route is quite difficult, in some places the road is steep, these places, especially in extremely low temperatures, are quite difficult to pass. Local residents additionally insulate their vehicles and even install a second windshield.
Besides frost, the second danger is bears. It is not uncommon for them to attack people. Therefore, you should not spend the night in abandoned settlements, especially without weapons. Walking into the forest without a guide is also not recommended. Some abandoned villages were built by prisoners; there are many adits and high radiation.
But in the summer there are no ticks in the region: due to the extremely low temperatures, these representatives of the fauna did not take root.
Gasoline in the Magadan region is expensive, and diesel fuel is even more expensive. This is due to the peculiarities of supply in the region. The further the settlement is from Magadan, the more expensive the fuel.
The Magadan region is the richest region of Russia with untouched lands. But the whole paradox is that people are fleeing from there. Today there is a real demographic catastrophe. This region was once a real currency forge of the entire country, but now it consists mainly of abandoned settlements.