The Omsk region is located in the southwestern part of Siberia. The development of this large region began in the 16th century, when the troops of Ataman Ermak came to the Siberian lands. Satellite maps of the Omsk region will help you get an idea of the location of the region, find its cities, roads and other objects. Using the online service you can find buildings, attractions, and train stations. It will prove to be an indispensable assistant when traveling and on a business trip.
The region neighbors Kazakhstan, as well as such Siberian regions as:
- Novosibirsk;
- Tomskaya;
- Tyumen
From north to south, the region is divided into 2 parts by the Irtysh River. On the map of the Omsk region with diagrams you can also find other rivers:
- Ishim;
- Tara;
- Osha;
- Om.
The southern regions are represented by steppe and forest-steppe landscapes, and in the north of the region there are vast swampy areas. The nature and wildlife of the region are unique. There are about 30 nature-protected areas in which wild animals, rare birds and fish live. In every corner of the region there are beautiful places, historical and architectural attractions, which can be found on a map of the Omsk region with districts.
Before you go to this region, research it using an online service. You can find out how to get to any locality by car - the map will indicate the desired route, which cities have rail connections and how to reach the region by air. In any area on the map of the Omsk region you can find interesting objects, monuments and nature reserves.
Districts on the map of the Omsk region
The region is divided into 32 districts. The northern regions have large areas, while the southern ones are smaller but densely populated. The main district of the region is Omsk. Large highways pass through it, which are indicated on the detailed road map of the Omsk region, and the Trans-Siberian Railway. You can also come here by air or water transport. In the Omsk region there is the Achair outpost - this is one of the first settlements that was built by Russian people.
If you move around the map of the Omsk region with settlements, you can find areas with unique and interesting sights:
- Lake Ulzhay - in Cherlaksky district;
- natural park "Batakovo" in Bolsherechensky district;
- St. Nicholas Monastery - in the Omsk region;
- Rock "Devil's Finger" in Gorky district.
If you are traveling around the region, then in each district, using a detailed map of the Omsk region, you can create your own route and visit interesting places. For those who are on a business trip, the online service will help them find hotels, enterprises, administrative institutions, and cafes.
Map of the Omsk region by district
The territory of the Omsk region is larger in size than many Western European countries. It occupies 139.7 thousand square kilometers, which is one fifth of Western Siberia, and is located in the southern part of the West Siberian Plain.
In the north and west, the Omsk region borders on the Tyumen region, in the east there is a border with the Novosibirsk and Tomsk regions. In the south and southwest it has a border with Kazakhstan. The Omsk region is divided into 424 municipalities: 1 urban district, 32 municipal districts, 26 urban settlements and 365 rural ones. 1.97 million people live in the Omsk region, of which 71.76% live in cities.
Omsk region. Online map (The dotted line indicates the boundaries of the area on the map)
Since the region is located in the northern hemisphere, the climate is harsh. Winter is characterized by low temperatures, with cold snaps occurring in spring and autumn. Temperatures are erratic and fluctuate wildly throughout the year. This is explained by the fact that the flat nature of the region allows air masses to move freely across its territory, both from the south and from the north. Within a few hours, there may be a change from warm weather to a sharp cold snap. The average temperature range from the coldest to the warmest month is 38 degrees. Moreover, over the vast territory of this region between the northern and southern parts, the temperature difference ranges from 1 to 3 degrees. The climate in different parts of the region is varied. The region is not inferior to Ukraine and the North Caucasus in terms of the number of sunny days. On average, the region's territory is arid; in winter the snow cover is small (up to 60 cm).
Districts of the Omsk region:
|
|
Map of the Omsk region by district
Cities and towns:
|
|
The largest cities in the region: Omsk with a population of 1 million 131 thousand people, Tara - 27 thousand people, Isilkul - 26 thousand people, Kalachinsk - 24, Tavrichesky - 14. It is estimated that the total number of rivers in the Omsk region is 4230 km. Among them, there are only 11 rivers with a length of more than 100 km. The powerful Siberian Irtysh River flows through the entire Omsk region; with the help of shipping, numerous economic connections are carried out between neighboring regions and Kazakhstan. Along with a large number of rivers, there are 16,000 large, medium and small lakes. Only 25 of them are large and have an area of more than 10 square meters. km. The region is distinguished by a huge number of swamps with a total area of more than 2000 hectares. The unique character of the nature of the Omsk region lies in the fact that from north to south there is a change in natural complexes: from taiga to steppe plains. There are 13 botanical reserves, 17 zoological reserves, one natural park and 99 natural monuments on the territory. The Bairovsky reserve, for example, is the oldest reserve in the Irtysh region, in which numerous species of birds, including waterfowl, and countless wild animals are preserved in their natural environment. Conditions have been created for the reproduction of beavers and otters. In the Omsk region you can get acquainted with 1,700 historical monuments (mounds, ancient settlements) and interesting modern buildings. Many have heard about Peipus Mountain, Ermak's Pier, Bogatyrsky Mounds, Mount Tara, Chekhov's Import and others. The Vrubel Museum of Fine Arts is widely known in Omsk - one of the largest in Russia. It contains a rare exhibit - Scythian gold. In the floodplain of the Bolshaya River there is the Bolsherechensky Zoo with an area of 19 hectares, which is the northernmost in the world (1,400 species of animals, 160 species of birds, reptiles, etc.). And in the Bird Harbor natural park in the center of Omsk there are 300 species of plants, 160 species of birds and more than 250 species of insects. At Lake Ik you can see the northernmost colony of pelicans. In the area of the village of Okunevo there are the most ancient underground ruins of a huge temple. Tourists are also interested in the Omsk fortress, built in 1716 by Swedish prisoners of war, and the oldest guardhouse building in Omsk with original decor. The first mansion with steam heating, built in 1902 by the merchant Batyushkin, has also been preserved in Omsk. The Museum of History and Local Lore in Omsk was founded in 1878 on the initiative of world-famous travelers and scientists. The exhibition is based on collections from expeditions from China, India, Central Asia, and Siberia. The Dostoevsky Literary Museum is located in the commandant's house. The writer was serving hard labor in Omsk. The atmosphere of the past is recreated by ancient houses and fortress gates to enter the city. 50 km from Omsk there is an ancient women’s Achairsky monastery.
Map of the Omsk region with cities and villages
There are 6 cities and more than 1.5 thousand villages and settlements in the region. The capital of the region is the city of Omsk. This is a million-plus city and a large industrial, commercial, sports and cultural center of the Irtysh region. If you enlarge the map of the Omsk region with cities and villages, you can see all the streets with house numbers. A large number of ancient architectural buildings have been preserved in Omsk. There are also modern sports facilities, theaters and museums.
The second most populous and most interesting city in terms of history and region is Tara. This is the 1st city built in the region. Currently, it is a settlement with preserved wooden architecture, and previously it was inhabited by merchants and industrialists who developed the lands of the region, built plants and factories, and financed the construction of railways and roads.
Small towns in the region include:
- Tauride;
- Kalachinsk;
- Isilkul;
- Nazyvaevsk.
A large number of people live in rural settlements, which are presented on the map of the Omsk region with villages. In small settlements, crop and livestock farming is carried out, and eco-tourism is actively developing.
Regions of the Russian FederationOmsk region- Geography
- Climate
- Relief
- Hydrography
- Aquatic biological resources
- Vegetation
- Soils
- Agriculture
- Districts of Omsk region
Geography.
The Omsk region is located in the southwest of Siberia. The territory area is 141,140 km2.
Climate.
Continental, moderately cold. Winters are long and harsh, summers are warm and short. The growing season is 153-162 days. The duration of the frost-free period is 127 days (May 16 - September 19). The establishment of snow cover occurs on November 12, melting on April 15, the maximum height (24 cm) is observed in March.
Relief.
It is located in the south of the West Siberian Plain, in the middle reaches of the Irtysh. The surface is a gently undulating plain (height up to 146 m), in the south there are typical ridge-like hills (ridges), which stretch for several kilometers. In the northern part there are vast wetlands.
Hydrography.
Surface waters.
≈ 2.1% of the area is under water, ≈ 14.4% is occupied by swamps. The water resources of the region are represented by the Irtysh River with its tributaries, oxbow lakes, small rivers, lakes, swamps, artificial ponds and groundwater. There are 2,929 rivers in the region, 15,479 km long, and 2,459 lakes with a total water surface of 177,103 hectares. The largest lakes are: Saltaim (surface area 147 km2), Tenis (118 km2), Ik (71.4 km2), Ebeity (83.3 km2). Lake Ebeity is salty.
The groundwater.
For domestic and drinking needs in the region, fresh and brackish groundwater with a mineralization of up to 3 g/dm3 is used. Their predicted resources are 3.8 million m3/day. The largest fresh groundwater resources are concentrated in the northern regions of the region, the smallest in the central and southern regions. In the south-eastern and south-western regions of the region there is practically no fresh groundwater. The explored reserves of groundwater for domestic and drinking purposes are approved in the amount of 67.85 thousand m3/day. In total, 19 deposits of groundwater for domestic and drinking purposes have been explored, mainly for several regional centers of the region, the cities of Omsk, Tara and the Chernoluchinsko-Krasnoyarsk resort area. The degree of use of proven groundwater reserves is low - out of 19 explored deposits, only 6 are exploited.
Aquatic biological resources.
The fund of used freshwater and other water bodies that can be used for fishery purposes in the region consists of rivers (61,537 hectares), lakes (190,313 hectares), and fish ponds (2,820 hectares). 326 km of the Irtysh River, 33 thousand hectares of floodplain and continental reservoirs, which is less than 1% of the stock of rivers and streams, and about 0.2% of the stock of continental reservoirs, are assigned to fish producers on the basis of licenses. Caught: whitefish, peled, large fish, burbot, ide, pike, bream, pike perch, carp, small fish, roach, perch, crucian carp.
Vegetation.
Subtaiga zone, forest-steppe and steppe. The vast majority of plant species inhabiting the territory are, to one degree or another, forage species. Forests occupy ≈ 32.3% of the area.
Soils.
The following are distributed by area: meadow solonetzes (hydromorphic) - 13.5%, meadow-chernozem solonetzic and solonchakous - 13.3%, tongue ordinary chernozems - 6.5%, sod-podzolic illuvial-ferruginous - 5.7%, meadow solonetsic and solonchakous - 5.7%, ordinary chernozems - 5.6%, transitional peat bog soils - 4.6%, acidic floodplain chernozems - 4.5%, residual carbonate chernozems - 4.3%, gray forest solodized (including .ch. with a second humus horizon) - 4.2%, lowland peat bogs - 3%, meadow-bog - 2.9%, sod-podzolic deep gleyic and gleyic (including surface gleyic) mainly deep - 2 .8%, sod-podzolic predominantly deep-podzolic soils - 2.3%, southern tongued chernozems - 2.3%, soddy-podzolic-gley soils with a second humus horizon - 2.2%, soddy-podzolic-gley soils - 2%, tongued chernozems and pocket leached - 2%, peat bog high - 2%, peat bog lowland and peat bog transitional (ridge-hollow complexes) - 1.8%, meadow (without division) - 1.7%, peat bog high and peat bog transitional (ridge-hollow complexes) - 1.1%, peat and peaty-podzolic-gley - 0.9%, southern chernozems - 0.7%, gley peaty and peaty podzols, mainly illuvial-humus - 0.6% , gray forest gleyic and gleyic - 0.6%, meadow-chernozem - 0.6%, meadow solonchaks - 0.6%, non-soil formations (water) - 0.4%, soddy-podzolic (without separation) - 0, 3%, light gray forest soils - 0.3%, soddy-podzolic soils with a predominantly deep second humus horizon - 0.2%, gray forest soils - 0.2%, podzolized chernozems - 0.2%, meadow solonetzes (semi-hydromorphic) - 0.2%, meadow-chernozemic solonetzic and solonchakous and meadow (semi-hydromorphic) solonetzes (round-spotted tuberculate complexes) - 0.2%, illuvial-ferruginous podzols (illuvial-low-humus podzols) - 0.1%, typical solonchaks - 0 .1%, taiga gley peat-humus (taiga peat-humus gley soils) -
Acidic soils are confined to the northern part of the region. Solonetzes, solonchaks and other saline soils, and complexes with their participation, are confined to vast lakeside depressions (Tyukalinskaya, Ebeytinskaya, Kurumbelskaya, Kamyshlovsky ravine), to neogenic lacustrine-aluvial plains (Om-Irtyshskaya, Sargatskaya, Alabotinskaya). The formation of solonetzic and saline soils is facilitated by poor drainage of rocks, close occurrence of aquitard and mineralization of groundwater. There is a rise in groundwater everywhere, which has led to an increase in the area of saline soils, as well as waterlogging and swamping of lands. The most complex area in terms of waterlogging and swamping is the central and northern part of the region. It is located in an area of close groundwater (1-3 m), numerous lakes and swamps.
Agriculture.
Farmland occupies ≈ 47.6% of the territory, its structure includes arable land ≈ 61.9%, perennial plantings ≈ 0.4%, hayfields ≈ 16.3%, pastures ≈ 18.8%.
Animal husbandry.
They breed cows (red steppe Siberian)), pigs (highrock), sheep, goats, horses, poultry (chickens, ducks, geese, turkeys), fur-bearing animals (silver-black fox), fish (sturgeon, salmon, salmon, muksun, trout, sterlet).
Plant growing.
They grow wheat (spring, winter), oats, barley, rye (winter), buckwheat, millet, corn, peas, flax (fiber, oilseed), sunflower, rapeseed, camelina, soybeans, potatoes, tomatoes, melons, pomaceous, stone fruits, nuts, berries, grapes, broad beans, perennial and annual herbs.
Trades.
Fishing, fur trapping (squirrel, muskrat, ermine).
Approximate calendar of agricultural work in the Omsk region
| 2 | Sowing spring wheat, corn, legumes, sunflower, fiber flax, planting potatoes, vegetables, sowing fodder beans, annual and perennial grasses; closing moisture | |
| 3 | Sowing wheat, barley, oats, legumes | |
| June | 1 | |
| 2 | Sowing corn (silage), oilseeds, fodder beans | |
| 3 | Procurement of feed | |
| July | 1 | Procurement of feed |
| 2 | Procurement of feed | |
| 3 | Procurement of feed; grain harvesting | |
| August | 1 | Harvesting winter grains; feed preparation |
| 2 | Procurement of feed; harvesting winter wheat; sowing winter crops | |
| 3 | Procurement of feed | |
| September | 1 | Harvesting of grains, vegetables, root crops, oilseeds; feed preparation; processing of plowed land; sowing winter crops |
| 2 | Harvesting of grains and legumes; feed preparation; sowing winter crops | |
| 3 | Harvesting grains, legumes, fiber flax, potatoes, vegetables | |
| October | 1 | Harvesting of grains and legumes |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| November | 1 | |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| December | 1 | |
| 2 | ||
| 3 |
Districts of the Omsk region
Azov German national region.
Located in the south of the region.
The territory area is 1400 km2. Poultry farming, dairy farming. They grow wheat and legumes. Bolsherechensky district.
Located in the east of the central part of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 4300 km2. The main rivers are the Irtysh and Bolshaya. grow grains. Bolsheukovsky district.
They grow grains and fiber flax.
Gorky district.
Located in the east of the central part of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 3 thousand km2. Located in the northern forest-steppe climate zone. The main river is the Irtysh. Meat and dairy cattle breeding, pig farming, poultry farming. They grow grains and corn. Znamensky district.
Located in the north of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 3700 km2. The main rivers are the Irtysh, Osha, Shish, Bolshoi Aev, Bolshoi Nyagov. Fiber flax is grown. Isilkul district.
Located in the southwest of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 2800 km2. The climate is continental. The average annual air temperature is +0.2°C. The average temperature in January is -18.6°C, in July +18.2°C. The average precipitation is 300-400 mm/year. Almost half of the precipitation falls in summer and reaches an average of 170 mm. Out of 5 years, 2-3 years are usually dry. In winter, there is little precipitation; the average snow cover in the region is 20-25 cm. The relatively monotonous flat surface of the region is broken by small relief forms: depressions, ridges, lake basins, ravines, gullies. There are no rivers in the region. Large lakes: Kamyshnoye, Krivoe, Solenoye, Ibitskoye, Kamyshlovo, Polovinnoye, Bolshoye Pervotarovskoye. Pike, crucian carp, perch, etc. are of commercial importance. The area is located in the southern part of the forest-steppe zone. The forests are represented by birch, birch-aspen forests and willow thickets. Chernozem soils are widely represented in the region. They are more often found in elevated forms of relief (ridges, ridges, slopes) and do not have signs of waterlogging. Meadow-chernozemic solonetzic soils are formed under waterlogged conditions and contain salts. They are observed in hollows and flat drainage depressions near lakes and swamps. Gray forest soils are common in birch and aspen groves. The peculiar nature of the surface, the presence of soils and the high level of mineralization of groundwater determine the widespread occurrence of saline soils in the region: solonchaks, solonetzes and solods. Dairy and beef cattle breeding, pig farming, poultry farming. They grow wheat, rye, barley, buckwheat, flax, sunflower, camelina, potatoes, vegetables, sugar beets (for feed). Kalachinsky district.
Located in the southeast of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 2800 km2. The main river is Om. Cattle breeding, pig farming, sheep farming, poultry farming. They grow grains and fodder. Kolosovsky district.
Located in the north of the central part of the Omsk region.
Territory area - 4800 km2. The main river is Osha. They grow grains. Kormilovsky district.
Located in the southeast of the region.
Territory - 1.9 thousand km2. Located in the southern forest-steppe climate zone. The main rivers are Om and Tarbuga. Meat and dairy cattle breeding, pig farming, poultry farming. They grow grains, corn, and vegetables. Krutinsky district.
Located in the west of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 5800 km2. Main lakes: Saltaim, Tenis, Ik. The main river is Osha. They grow grains. Lyubinsky district.
Located in the southwest of the central part of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 3300 km2. Cattle breeding, poultry farming, pig farming. They grow grains. Maryanovsky district.
Dairy farming.
They grow grains and vegetables. Muromtsevo district.
Located in the east of the Omsk region.
Territory area - 6700 km2. The main rivers are Tara, Bergamak, Upper Tunguska, Lower Tunguska. Beef cattle breeding. They grow wheat and flax. Odessa region.
Located in the south of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 1800 km2. Poultry farming. Okoneshnikovsky district.
Buckwheat is grown.
Omsk city district.
Located in the south of the central part of the Omsk region. The territory area is 566.86 km2.
The climate is continental.
They raise cows, pigs, horses, sheep, and goats.
They grow wheat (spring), sunflower, potatoes (≈ 56.7% of the sown area (2020)), tomatoes (≈ 10.1% of the sown area (2020)), melons, pomaceous, stone fruits, nuts, berries, grape. Omsk region.
Located in the south of the central part of the Omsk region.
Territory area - 3590.72 km2. The territory of the district is located along the middle reaches of the Irtysh River and the lower reaches of the Om River, in the forest-steppe zone. Poultry farming (chickens), pig farming. They grow wheat, barley, buckwheat, peas, and vegetables. Poltava district.
Located in the southwest of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 2800 km2. They grow wheat and sunflower. Russko-Polyansky district.
Located in the southeast of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 3300 km2. They grow grains and buckwheat. Sargatsky district.
Located in the center of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 3800 km2. The main river is the Irtysh. Pig farming. They grow grains. Sedelnikovsky district.
Located in the northeast of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 5221.37 km2. The main rivers are Uy, Shaitanka, Maly Shish, Shish. They grow wheat. Tavrichesky district.
Located in the south of the Omsk region.
The territory area is 2735.89 km2. The main river is the Irtysh. Pig farming. Tyukalinsky district.
Located in the west of the central part of the Omsk region.
Territory area - 6400 km2. The main river is Osha. They grow grains. Ust-Ishimsky district.
Located in the north-west of the Omsk region.
The area of the region is 7900 km2. The main rivers are the Irtysh, Ishim, Bicha, and Bolshaya Tava. They grow grains. Sherbakul district.
Located in the southwest of the Omsk region. Territory area - 2321.82 km2. Poultry farming.
Information sources:
- Peasant Gazette
- Wikipedia
- Omsk region on the map
- Unified State Register of Soil Resources of Russia
- Federal State Statistics Service
- Rosreestr
- EMISS
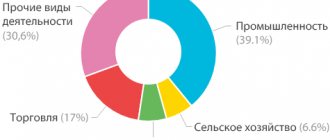
Economy and industry of the Omsk region
The economic component of the region is represented by several industries and agriculture. Enterprises of such industries as:
- military;
- chemical;
- aerospace;
- mechanical engineering;
- petrochemical
Enterprises that can be found on Yandex maps of the Omsk region produce a wide variety of goods:
- furniture;
- Food;
- beverages;
- Construction Materials;
- clothes;
- shoes.
Agriculture makes a large contribution to the regional budget. Potatoes, legumes, cereals, and fodder crops are grown in the region. Food industry enterprises produce semi-finished products and other goods from animal products. Cattle, poultry, and pigs are raised in the region.
Large retail facilities belonging to federal retail chains are concentrated in the Omsk region of the region. The service sector is also well developed. There are a large number of hotels, restaurants, and entertainment centers in the regional capital and other cities.