For other uses, see Slavyansk (disambiguation).
City in Krasnodar Krai, Russia
| Slavyansk-on-Kuban Slavyansk | |
| Town[1] | |
| Welcome sign at one of the entrances to the city | |
| Flag Coat of arms | |
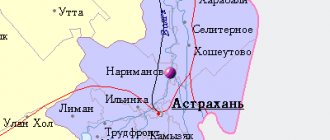
| Location of Slavyansk-on-Kuban | |
| Slavyansk-on-Kuban Location of Slavyansk-on-Kuban Show map of Russia Slavyansk-on-Kuban Slavyansk-on-Kuban (Krasnodar region) Show map of Krasnodar region | |
| Coordinates: 45°15′N 38°07′E / 45.250°N W. 38.117°E / 45.250; 38.117Coordinates: 45°15′N 38°07′E / 45.250°N W. 38.117°E / 45.250; 38.117 | |
| A country | Russia |
| Federal subject | Krasnodar region[1] |
| Based | 1865 |
| City status from | 1958[2] |
| Height | 7 m (23 ft) |
| population (2010 Census)[3] | |
| • General | 63,842 |
| • Evaluate (2018)[4] | 66,285 (+3.8%) |
| • Classify | 247th in 2010 |
| Administrative status | |
| • Subordinate | Town of Slavyansk-on-Kuban[1] |
| • Capital from | City of Slavyansk-on-Kuban[1], Slavyansky district[1] |
| Municipal status | |
| • Municipal district | Slavyansky municipal district[5] |
| • Urban village | Urban settlement Slavyanskoe[5] |
| • Capital from | Slavyansky municipal district[5], Slavyanskoye urban-type settlement[5] |
| Timezone | UTC + 3 (MSK [6]) |
| Postal code(s)[7] | 353560 |
| OKTMO I WOULD | 03645101001 |
| Web site | Sitislav.RU |
Slavyansk-on-Kuban
(Russian: Slavyansk-na-Kubani) is a town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located in the Kuban Delta. Population: 63,842 (2010 Census);[3]64,136 (2002 Census);[8]57,790 (1989 Census);[9]56,000 (1975).
Story
Slavyansk arose in Middle Ages as a Kop
or
Coparia
, a Genoese trading outpost controlled by the Ghisolfi family.
After the fall of Genoese power in the Black Sea region, the site was abandoned until 1747, when the Crimean Khanate erected a small fort, known in Russian sources as Kopyl
.
After the conquest of the Taman Peninsula by the Russian Empire, the Tatar fort gave way to the Cossack village
from
Kopylskaya
.
In 1865 it was renamed the Slavic Regiment, stationed here under Catherine the Great. In 1958, it was incorporated as the city of Slavyansk-on-Kuban (named to distinguish it from the city of the same name in Ukraine).[ citation needed
]. The history of Slavyansk dates back to the end of the 18th century. This city was a fortress founded by General Suvorov to protect the southern borders of Russia. In 1865 the fortress became a Cossack village. During World War II, this city was occupied by the Germans in 1942-1943, and in 1943 it was re-occupied by the Red Army. The city has monuments to those killed in the war.
According to the 1926 Soviet census, more than 69% Ukrainians lived in the city.[10]
Slavyansk-on-Kuban
The magnificent, flourishing city of Slavyansk-on-Kuban with a total area of more than 4 thousand hectares and a population of over sixty-four thousand people, today is a regional center, a significant unit in the development of Kuban. It stands on important transport arteries; roads to the ports of Novorossiysk, Temryuk, the port of Kavkaz pass through it, and the city is crossed by a railway line.
Modern Slavyansk-on-Kuban is a hard-working city. A city of oil workers and rice farmers, gardeners and builders, workers in processing industries and entrepreneurs. The city can rightly be called a student city. The Slavyansk-on-Kuban State Pedagogical Institute has been operating for more than ten years, and the Slavyansk Agricultural College has been producing qualified specialists for about 80 years. Medium and large businesses are widely developed in the city; there are more than 1,500 enterprises and more than 3,000 entrepreneurs. Successful, large enterprises contribute to the development of the city, in particular, Neftegaztenology-Energy OJSC, Cementnaya Transportnaya LLC, Slavyansky Bakery CJSC, Slavyanskaya Road Mobile Mechanized Column CJSC, Slavyansk Passenger Motor Transport Enterprise LLC, Maslosyr OJSC, OJSC "Kubrisvodstroy", CJSC Slavyansky, LLC "Gorvodokanal", OJSC Garment Factory "Slavyanskaya".
The city attracts people from all over the country with its climate, recreational conditions and hospitality of its residents; it delights the eye with wide and straight streets, magnificent squares, an abundance of flowers and greenery, new buildings in residential areas and architectural buildings of the last century.
A network of cultural institutions has been created in the city: a local history museum, an art gallery, a nature museum of the Azov region, children's art schools, interest clubs, an art school, a library system and a cinema network. The city is proud of its artistic groups: the pop symphony orchestra, the choreographic ensemble “Rhythms of the Planet”, the sacred music choir, the violin ensemble “Cantabile”, the male Cossack ensemble “Nugget”, VIA “Chance” and others. He is also proud of world-class athletes, such as Evgeniy Lukyanenko, world champion in athletics, Sergei Vodopyanov, world champion in boxing.
A network of healthcare institutions is actively developing in the city. Streets are being built, houses, shopping and entertainment complexes are being built. Many generations of Slavs lived and worked on this land, decorating it with their labors. And today, continuing the tradition of our ancestors, we are improving and greening our beautiful city.
In 2006, the Heraldic Commission under the President of the Russian Federation approved the coat of arms of the city of Slavyansk-on-Kuban, and in 2007 - the flag.
Toponymy
The name of the city comes from the name of the village of Slavyanskaya in 1958.[2] Slavyansk already existed since the times of the USSR in the Donetsk region, so the clarification “-na-Kuban” was added to the name of the city. The name of the village was given by the name of the fortification “Slavic Feldshanets” of the Slavic Hussars, which was under the command of Alexander Suvorov on the right bank of the Kuban.
In different sources, the name “Slavyansk” is made differently - by the first and second syllable, but local residents adopted the name Slavyansk by the first syllable.
How to get to Slavyansk-on-Kuban?
You can get to Slavyansk-on-Kuban by private car. To do this, tourists need to drive along the M4 Don federal highway and the A289 highway. It is best to plan a route in advance.
The airport in Slavyansk-on-Kuban is closed. The nearest operating airfield is Vityazevo, which is located in Anapa. The distance from the resort town to the airport is 94 km (approximate travel time - 1 hour 31 minutes).
The Protoka railway station is located in Slavyansk-on-Kuban. Long-distance trains and commuter trains pass through the local railway station.
The city of Slavyansk-on-Kuban has its own bus station, which is located at st. Kovtyukha, 120. The bus station building is located near the City Administration and the Settlement Administration.
Economy
- Petroleum products production
- Food industry: wine, canning, butter, cheese, rice and grain, poultry farms.
- Light industry: garment factory
- Production of building materials
Agriculture
The Slavyansky district is one of the largest agricultural regions of Kuban with a predominance of agriculture. Grain crops occupy two-thirds of the sown area. The leading direction is rice production. More than 30% of the total Kuban rice harvest is harvested in the Slavyansky region. Agricultural products are widely known in the region and beyond. This is the largest garden in Europe. In terms of gross harvest of fruits and berries (annual production volume is more than 30 thousand tons), the company ranks first in the region (26% of the total volume). Livestock farming and fishing are also developed.
Education
There are 91 educational institutions, including 50 schools.
- Branch of Kuban State University
- Slavic Agricultural College
- Vocational school No. 45
- Vocational School No. 20
- Slavic branch of Novorossiysk Medical College
- Slavic branch of the Technological, Economic and Legal College named after. A.A. Vyazemsky
- Branch of Moscow State University of Technology and Management. K. Razumovsky
- Branch of the Moscow State Technological Academy
- Anapa branch Industrial-technical
Festival of Slavic Culture
Of all the holidays of the Slavic calendar, the Festival of Slavic Culture is, without a doubt, the most important and colorful. The full name of the holiday is the Day of Slavic Literature and Culture. There are many talented people at the festival. Guests from near and far abroad, residents of Kuban and other regions of Russia come to the Slavic region to share a piece of their soul, carefully preserving the wealth of national cultures. A lot of pies, soups and dumplings are prepared. During the festival there is a Slavic hut. Preserving traditions in this region is very important. People are proud of the traditions of their country, so they pass them on from ancestors to descendants. Organizers are the Federal Agency for Culture and Cinematography of the Ministry of Culture and Mass Communications of the Russian Federation, the regional branch of the All-Russian political party "United Russia", the administration of the Krasnodar Territory, the administration of the Slavic Territory. The history of the festival began in 2004, when the provincial city of Slavyansk with a population of 60 thousand dared to hold a show of Slavic culture on an international scale. Over the course of four years, the festival has gained popularity, constantly increasing the number of participants. This year the city again welcomes guests from different countries so that they can share the wealth of national cultures and feel part of the Slavic community. A traditional procession of delegations and a parade of brass bands, a big dance of friendship and an incendiary extravaganza, a mini-festival “Filling the Apple” on the territory of the agro and a festival of children’s groups “Joy”. , the entertainment program “Dancing Until the Morning”, as well as a gala concert and a grandiose fireworks display in the festival program.
Recommendations
Notes
- ^ a b c d f g gram
Reference information No. 34.01-707 / 13-03 - ^ a b
“General information” (in Russian). Retrieved February 24, 2022. - ^ a b
Federal State Statistics Service of Russia (2011).
“All-Russian Population Census 2010. Volume 1" [All-Russian Population Census 2010, vol. 1]. All-Russian Population Census 2010 [All-Russian Population Census 2010]
(in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. - "26. The size of the permanent population of the Russian Federation by municipalities as of January 1, 2022.” Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2022.
- ^ a b c d f
Law No. 775-KZ - "On the calculation of time." Official Internet portal of legal information
(in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2022. - Post office. Information and computing center of OASU RPO. ( Post office
).
Search for postal facilities ( Search for postal facilities
) (in Russian) - Federal State Statistics Service of Russia (May 21, 2004). “The population of Russia, the constituent entities of the Russian Federation as part of federal districts, urban settlements, urban settlements, settlements, settlements of 3 thousand or more people.” [Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal subjects, districts, urban settlements, rural settlements - administrative centers, rural settlements with a population of more than 3000 people] (XLS). All-Russian Population Census of 2002 [All-Russian Population Census of 2002]
(in Russian). - “All-Union Population Census of 1989. The actual population of union and autonomous republics, autonomous regions and districts, territories, regions, urban settlements and villages-Kuban News”, No. 152, September 18, 2004 (Legislative Assembly of the Krasnodar Territory. Law No. 775 -KZ dated September 16, 2004 On establishing the boundaries of the municipal formation Slavyansky district, on assigning it the status of a municipal district, on the creation of municipal formations - urban and rural settlements within it and on establishing their boundaries
As amended by Law dated 06/03/2009 No. 1765- KZ.
On introducing amendments to a number of legislative acts of the Krasnodar Territory on establishing the boundaries of municipalities
... Valid from the date of official publication.).
Links[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ abcdefg Reference information No. 34.01-707 / 13-03
- ^ B "General information" (in Russian). Retrieved February 24, 2022.
- ^ a b Federal State Statistics Service (2011). “All-Russian Population Census 2010. Volume 1" [All-Russian Population Census 2010, vol. 1]. All-Russian Population Census 2010 [All-Russian Population Census 2010]
. Federal State Statistics Service. - "26. The size of the permanent population of the Russian Federation by municipalities as of January 1, 2022". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2022.
- ^ abcde Law No. 775-KZ
- "On the Calculation of Time". Official Internet portal of legal information
. June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2022. - Post office. Information and computing center of OASU RPO. ( Post office
).
Search for postal service objects ( postal Search for objects
) (in Russian) - ↑
Federal State Statistics Service of Russia (May 21, 2004).
“The population of Russia, the constituent entities of the Russian Federation as part of federal districts, urban settlements, settlements, settlements of 3 thousand or more people” [Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal districts, districts, urban settlements, rural settlements - administrative centers and rural settlements with a population of more than 3,000 people] (XLS). All-Russian Population Census of 2002 [All-Russian Population Census of 2002]
. - “All-Union Population Census of 1989. The current population of union and autonomous republics, autonomous regions and districts, territories, negative phenomena, urban settlements and rural district centers” [All-Union Population Census of 1989: current population of union and autonomous republics, Autonomous regions and districts , territories, regions, districts, towns and villages performing the functions of district administrative centers. All-Union Population Census of 1989 [All-Union Population Census of 1989]
.
Institute of Demography of the National Research University: Higher School of Economics [Institute of Demography of the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. 1989 - via Demoscope Weekly
. - Slavyansk-on-Kuban. Encyclopedia of Ukraine.
Sources [edit]
- Department for interaction with local government of the Administration of the Krasnodar Territory. Reference information No. 34.01-707 / 13-03 dated May 23, 2013 “Register of administrative-territorial units of the Krasnodar Territory.” (Department for interaction with local government bodies of the Krasnodar Territory administration. Reference information No. 34.01-707 / 13-03 dated May 23, 2013, Register of administrative-territorial units of the Krasnodar Territory
.). - Legislative Assembly of the Krasnodar region. Law No. 775-KZ of September 16, 2004 “On establishing the boundaries of the municipal formation of the Slavyansky district, giving it the status of a municipal district, the formation of municipal formations within it - a city and an urban settlement - and establishing their boundaries,” as amended. Law No. 1756-KZ of June 3, 2009 “On amendments to certain legislative acts of the Krasnodar Territory on establishing the boundaries of municipalities.” Came into force on the date of official publication. Published: “Kuban News”, No. 152, September 18, 2004 (Legislative Assembly of the Krasnodar Territory. Law No. 775-KZ of September 16, 2004 On establishing the boundaries of the municipal formation Slavyansky district, on assigning it the status of a municipal district, on the creation of municipal formations - urban and rural settlements in its structure and on the establishment of their boundaries
in the new edition of the Law of June 3, 2009 No. 1765-KZ “
On amendments to certain legislative acts of the Krasnodar Territory on the establishment of boundaries of municipalities.”
Valid from the date of official publication. ).