You may have heard about a Russian city like Novy Urengoy: someone was passing through there, and some still live permanently today. However, if you ask a person to tell about this settlement and even show its location on the map, most will fall into a stupor. To prevent this from happening, in this article we will tell you everything about Novy Urengoy: what region it belongs to, where it is located, what its history is and what both visiting tourists and indigenous residents can pay attention to here.
One of the cities of Western Siberia: general information
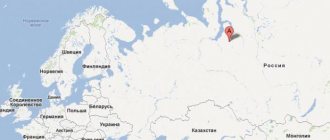
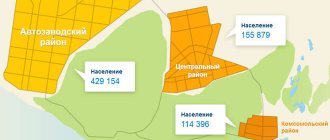
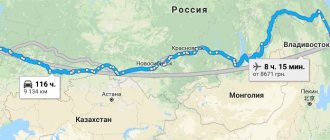
The city of Novy Urengoy - what region does it belong to? To Tyumen, which, in turn, is a constituent unit of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The city of Novy Urengoy is the largest populated area in the district and one of the few that is ahead of the administrative center of its subject both in industrial potential and in population (we are talking about comparison with Salekhard). The city discussed in this article is 450 kilometers east of the latter; It is separated from Moscow, located in the northeast of the capital, by 2,350 kilometers. In addition, residents of the city of Novy Urengoy, unlike Muscovites, live in a different time zone: for example, the New Year and other holidays are traditionally celebrated 2 hours earlier. Today the city is home to about 116 thousand people. Being a key link in the largest gas-bearing region, Novy Urengoy, the location map of which will be presented below, is unofficially called the gas-producing capital of the country.
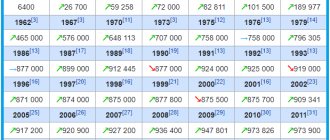
Population [ ]
| Population | ||||||
| 1989 | 2002 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
| 11 868 | ↘ 9329 | ↗ 9404 | ↗ 10 066 | ↗ 10 079 | ↗ 10 446 | ↗ 11 018 |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
| ↘ 10 817 | ↘ 10 268 | ↘ 10 190 | ↘ 10 082 | ↗ 10 092 | ↘ 9927 | |
Surrounding area
On the map, Novy Urengoy is located on the banks of the Evo-Yakha River, which is a tributary of the Pura. There are also 2 other rapids flowing through the city: Sede-Yakha and Tamchara-Yakha, which conditionally divide the settlement into Northern and Southern parts. The territory of urban areas is surrounded on all sides by the Purovsky district and heavily swampy areas. In total, Novy Urengoy (which region the city belongs to and what its general current position is has already been described above) occupies an area of 113 square kilometers. The Arctic Circle already begins 60 kilometers north of it.
Heat supply [ ]
Heat supply is provided from six boiler houses, the main volume of thermal energy for the village is generated by boiler houses 1, 2 and 3, the rest work for local facilities and in support mode. The level of heat supply provision is 100%. The coolant is transported through a pipeline system with adjustment of hydraulic parameters at 12 booster pumping stations No. 10, No. 11, No. 12, No. 21, No. 33, No. 42, No. 55, No. 65, No. 66, No. 85, No. 93, PNS " School". The production and transmission of thermal energy is provided by the Teplo branch of Yamalkommunenergo OJSC in the Purovsky district. Based on the material of the walls of the house, they can be divided into 3 groups:
Source
Climatic conditions
So, if it has now been clarified which area Novy Urengoy belongs to, it’s time to move on to analyzing provisions that have more practical significance for humans - for example, what is the situation with the weather and average temperatures? The climate of the city can be characterized as sharply continental. What does this mean? Since this settlement is located at the intersection of 2 climatic zones of the forest-tundra zone, subarctic and temperate, there is a severe winter, the duration of which reaches 9 months, and a cool summer, which lasts on average only for a period of just over 1 month. Important factors that influence weather conditions and shape the climate include the presence of permafrost, the city’s proximity to the sea, as well as the continuous circulation of Atlantic air masses. The average temperature in January is -21.7 degrees, in June - +9.1; at the same time, the relative air humidity is 78%, and the average wind speed reaches only 3.4 m/second. Frequent temperature changes in Novy Urengoy (the map of Russia helps to analyze all the conditions and factors shaping the climate) are accompanied by blizzards, blizzards, and blizzards. Most of the flat terrain of the settlement is covered with permafrost ice, which in the summer thaws to a depth of only 1 to 2 meters!
Infrastructure of Nur - a paradise in three dimensions
As they say, we won’t take it with one, but with the other. And if the natural conditions of the city, with their harshness, are not conducive to a joyful stay in it, then the infrastructure of New Urengoy, on the contrary, is thought out to the smallest detail for the joy and convenience of local residents. Moreover, this can be said with confidence both about transport and about the industrial and social infrastructure of Nura - a kind of paradise in three dimensions.
Thus, Novy Urengoy can safely boast of 100% availability of all means of transportation. At the same time, air transport has always been and remains the most popular in the city. Today, the local airport receives aircraft from Moscow (3-5 flights daily), the northern capital - St. Petersburg (at least a flight per week), as well as Tyumen, Yekaterinburg, Samara, Salekhard, etc. During the “warm period”, seasonal flights operate between Novy Urengoy and Krasnodar, as well as Nur and Mineralnye Vody.
No less developed in the gas capital is the railway service, represented mainly by Russian Railways trains. So, a train departs from Urengoy to Moscow every day; according to this message, the train also runs on schedule. In addition, trains depart from the Urengoy station to Tyumen, Yekaterinburg, Kazan, etc., and the railway connection itself plays an important role in freight turnover. The local river port, located in Korotchaevo and being a transport artery between the cities and towns of the Yamal-Nenets Autonomous Okrug and the Northern Sea Route, also plays an equally important role in the city’s economy. The Urengoy River Port bears the lion's share of cargo delivery for local construction and gas production enterprises.
The city's transport network is also very developed: in addition to the main roads crossing the territory of Nur, the city has bypass routes, and in its southern part a local viaduct was built for optimal transport interchange.
That is why there are practically no traffic jams in Novy Urengoy, with the exception of a slight congestion of the highway in the morning hours (from 7 to 9 am), and the main ones are caused either by accidents on the roads or by the “slipping” of freight trains under the viaduct. The road surface in the city itself is of high quality; moreover, in “problem areas”, repair work is carried out every summer and new asphalt is laid. In recent years, a tradition has emerged every summer to expand the highway in some area of Urengoy.
In addition, due to the city’s low supply of garages, the Urengoy administration annually increases the area of “parking spaces” near houses by increasing the driveways in front of them.
As mentioned earlier, housing and communal services are not lagging behind: the areas adjacent to houses, as well as the entrances to them, are regularly cleaned by Urengoyzhilservice employees, and in winter they are cleared of snow. Actually, this diligence is partly caused by the high prices for utilities in Nura, where, for example, 1 cubic meter of hot water costs Urengoy residents on average 104 rubles, cold water - 28 rubles, with the cost of a cubic meter of sewerage being 31 rubles. And the very “maintenance” of housing, for example, a small one-room apartment, will cost about 1,400 rubles per month; a slightly smaller amount, about 1,150 rubles, will have to be paid for its monthly heat supply. At the same time, the cost of 1 thousand cubic meters of natural gas costs Urengoy residents 2,686 rubles, which is only 27 rubles per month for the maintenance of one stove. Average prices for electricity in the city are 1.7 rubles per 1 kWh.
Social infrastructure is also very developed in Novy Urengoy. There are more than 38 preschool institutions, 24 schools in the city, including a local gymnasium, a secondary evening school and 2 elementary schools. The doors of the local school are open for children with developmental disabilities, and Urengoy youth can receive secondary vocational education in a number of local schools, including the gas industry technical school. In addition, 7 branches of Russian universities have been opened in the city, the most important among which is the Yamal Oil and Gas Institute.
Nur's healthcare sector is represented by 11 medical institutions, with the largest of them being the municipal city multidisciplinary hospital. In addition, the gas capital has 17 sports institutions, as well as a number of city palaces and cultural and sports centers.
The beginning of the story
It’s a pity that facts about the development of cities and, in particular, Novy Urengoy are not indicated on the map of Russia - there won’t be enough space, and the purpose of these reference books is different. Few people would think of studying the historical formation of this particular settlement, and it would be in vain! The history of the city reveals a lot of interesting things: from the very beginning it was closely intertwined with the development of the Urengoy gas field, discovered in June 1966. However, in fact, the roots of the city’s formation must be sought even earlier, namely in 1949, when, by order of Stalin, construction of a transpolar railway began in the subpolar tundra zone for the movement of trains along the Salekhard-Igarka route. It was not the plan of the builders, who mostly belonged to the rest of the thousands of camp prisoners sent to build the road, to linger at the former Urengoy trading post. However, Stalin died, the construction work was curtailed and forgotten, the built tracks were called “dead,” but for Urengoy it was a turning point: it was the once unfinished railway forks that helped drillers and seismic explorers discover deposits in these lands and quickly develop them. In January 1966, the opening of a new Urengoy structure took place here. The pioneering team was a company of employees of the seismic station V. Tsybenko, which occupied the barracks of a once abandoned camp where Gulag prisoners had previously lived.
Living sector [ ]
Modern residential development in the village of Urengoy
The residential area of the village of Urengoy is a group of blocks with an area of 12-18 hectares, built up mainly with 2-story wooden houses. Single-storey buildings are concentrated mainly in the Molodezhny quarter and in the village of Taezhny, located 750 m east of the main residential area of the village of Urengoy. According to the schematic map of climatic zoning for the construction of Urengoy, it belongs to the 1st climatic region (subregion I B). The climate of the area is harsh, subarctic, with long (about 7 months) snowy, frosty winters, winds, blizzards and short (1.5-2.0 months) cool, rainy summers. The climate is characterized by ultraviolet deficiency with ultraviolet “starvation” for 4 months (November-February) and biologically active solar radiation for up to 2 months (June-July). According to observations at the Urengoy meteorological station, the average annual air temperature is minus 7.8 °C, the average monthly temperature in January, the coldest month, reaches minus 26.4 ° C. The absolute minimum in January is minus 56 °C. The housing stock of Urengoy consists of 286 residential buildings. Of the total number of houses, 208 are municipally owned, 70 are privately owned, and 8 houses have departmental ownership. The bulk of privately owned houses are located in the Molodezhny and Taezhny microdistricts.
The way forward
Subsequently, active mining continued here: in June 1966, master V. Polupanov and his team drilled the first exploration well. It was after this that a footnote appeared on the map of the country indicating the unique Urengoy natural gas field. September 1973 was marked by the fact that on the site of a city that did not yet exist at that time, a peg was driven in with a sign and a symbolic inscription on it: “New Urengoy” (we, the descendants, now know where the city is located). In December, construction began on a settlement familiar to Russians today. The village developed rapidly, which was associated with an increase in the activity of the gas produced in it. In 1980, Novy Urengoy, previously not considered a city (to which region this place belongs and what its historical formation is, now everyone can answer) finally received the long-awaited status and was now called a city of district significance! Since 1984, gas from here began to be exported to Western Europe using the Urengoy - Pomary - Uzhgorod gas pipeline built in 1983.
In November 1984, the village of Korotchaevo came under the authority of Novy Urengoy and the city council representing it at the administrative level, and in May 1988, the village of Limbayakha. As a municipal entity, Novy Urengoy was formed only in January 1996 with reference to one of the relevant laws of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, and in 2004 the above-mentioned villages ceased to exist as independent administrative-territorial elements and became part of the city of Novy Urengoy. As a result, the city with a length of 80 km turned into one of the longest in the whole world!
Serious measures
An interesting fact is that in 2012 the city actually became closed, given that there was no actual legal basis for this. Entry into the city could only be done with a special pass. Such drastic measures were needed because the crime level in this territory was approaching a critically high level. Various terrorist organizations were active here, and therefore the situation had to be resolved on an emergency basis. There is also an unconfirmed hypothesis that this practice of a permit system was introduced to regulate population migration and limit the internal and external “turnover” of residents. Be that as it may, such a system in Urengoy, whose name translated from one of the local Nenets dialects means “lost place,” lasted about six months and then was abolished.
Economy [ ]
Stele at the entrance to Urengoy
The village of Urengoy has a stable financial and economic base, the only disadvantage of which is the lack of diversification of the local economy and its connection to the fuel and energy complex. In 2005, the number of enterprises and organizations operating in the territory of the municipal formation of the Urengoy village amounted to 103 units, including 4 enterprises of federal ownership, 14 - municipal, 85 - private. The largest share in terms of the number of enterprises is occupied by the following sectors of the economy:
The total amount of investment in fixed assets in the municipality of Urengoy at the end of 2005 amounted to 713.87 million rubles, including 574.85 million rubles. was financed from the enterprises' own funds, 90.12 million rubles. — at the expense of the district budget, 48.9 million rubles. - at the expense of the local budget. In 2007, the volume of investments in fixed capital from the local budget amounted to 3.17 million rubles.
Industry
Novy Urengoy, being a fairly young city, manages to demonstrate extraordinary industrial potential. Thus, within the settlement there are 3 pillars of the gas production industry, each of which is a subsidiary: Tyumenburgaz, Yamburggazodobycha and Urengoygazprom. They account for about 74% of all gas produced in the country! Construction work to restore railway lines is being carried out by the Yamal Railway Company. 80% of river transportation occurs at the Urengoy river port, which has dozens of ferries and tractors.
Attractions
Among the key places in Novy Urengoy, a map with the streets of which will be offered below, we can highlight the Museum of Fine Arts, a multifunctional, modern and technologically advanced station commissioned in 2015, the largest fountain in the Far North, visually reminiscent of a sail. On the roof of the shopping mall, which is designed in an eye-catching color scheme, visitors can see a model of a real rotary-wing aircraft. The city is also home to monuments and temples - real examples of architectural art and architecture (for example, the Epiphany Cathedral, built in 2015, which is the tallest building in the city).
Education
There are many universities operating on the territory of New Urengoy, including:
- branch of the Moscow State Open University;
- branch of Tyumen Oil and Gas University;
- branch of the Tobolsk State Pedagogical Institute named after. DI. Mendeleev;
- branch of Tomsk State University of Radioelectronics and Control Systems;
- branch of the Moscow Open Social University (Institute) and others.
As you can see, here, in one of the cities of the Tyumen region, you can not only live, but do it successfully: study, work and make plans for the future.