Hello, dear colleague! To effectively participate in tenders (government procurement), it is necessary to narrow the search for information about ongoing tenders to a specific region or region.
Why do you need to do this? Firstly , the unified information system (www.zakupki.gov.ru) provides information on ongoing tenders in all constituent entities of the Russian Federation and tracking the emergence of new data in all regions is a labor-intensive and useless task; secondly , you need to take into account your capabilities (the company’s capabilities) to fulfill contractual obligations in the event of your victory. Suppose your company is located in Moscow, and the Customer is in the Sakhalin region, you yourself understand that these are additional costs for transportation, travel expenses, etc. Thirdly , the Customers themselves are quite skeptical about procurement participants (suppliers) from other regions and are doing everything possible to ensure that the contract goes to “their own”. Therefore, you need to clearly define for yourself where you will participate and not waste your time and energy on processing all the other information.
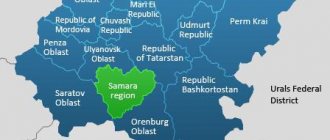
Below I have provided data on the federal districts and their constituent entities of the Russian Federation. I hope this information will be useful to you, because... this is the main navigation tool for searching information in the Unified Information System (UIS).
1.3. Natural resource potential
Minerals
Oil is one of the most significant mineral resources in the Samara region. The share of the Samara region in oil production in Russia is 2.3%.
As of January 1, 2007, residual recoverable oil reserves in the region exceed 300 million tons. Cumulative production since 1936 amounted to 1118 million tons. Currently, about 20.0% of the original oil reserves remain in the bowels of the Samara region . If current production levels are maintained, oil reserves will last for approximately 35 to 40 years. The entire territory of the Samara region is geologically promising for the search for oil and gas deposits.
Every year in the Samara region, 170-180 million m³ of associated petroleum gas is flared. The main goal is to achieve a 95 percent level of associated petroleum gas utilization in the fields of the Samara region. At the same time, several goals are achieved at once - the enterprises of the petrochemical complex are provided with raw materials and the environmental situation in the Samara region is improved by reducing emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere.
In addition to hydrocarbon raw materials, deposits of such minerals as molding sands, cement raw materials (limestones, dolomites, clays, opoka), as well as common minerals - brick and expanded clay, construction sands, building stone, raw materials for lime are being developed in the Samara region . The subsoil of the Samara region also contains reserves of chalk, gypsum and anhydrite, rock salt, native sulfur, phosphorites, natural bitumen, diatomites, zeolite-containing rocks, and peat.
It is necessary in the near future to involve the existing potential of mineral raw materials in industrial development to meet the increased needs of the local economy, especially housing and road construction.
From Wikipedia - the free encyclopedia
| Timezone | MSK+1 (UTC+4) |
| Economy | |
| GRP | RUB 1,510.5 [2] billion (2022) |
| • place | 11th place |
| • per capita | 473.8 [5] thousand rubles. |
| Population | |
| Population | ↘ 3,154,164 [6] people (2022) |
| Density | 58.88 people/km² |
| Digital IDs | |
| ISO 3166-2 code | RU-SAM |
| OKATO code | 36 |
| Code of the subject of the Russian Federation | 63 |
| Official site | |
It borders in the west with the Saratov and Ulyanovsk regions, in the southeast with the Orenburg region, in the north with the Republic of Tatarstan, and in the south with Kazakhstan at a single point. Due to the proximity of the West Kazakhstan region of Kazakhstan, part of the Bolshechernigovsky district has the status of a border territory. Formed on May 14, 1928 as the Middle Volga region. In 1929 it was renamed the Middle Volga region, in 1935 - the Kuibyshev region. In the period from December 5, 1936 to May 16, 1992 [8] it was called the Kuibyshev region. Preceding the constitutional changes, the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR on the return of the region to the name Samara was published on January 25, 1991. Historically, the region was preceded by the Samara province, formed in 1851. Source | |
Regions and administrative centers of the Volga Federal District
| Region Volga Federal District | Area, km² | Population (persons) | Administrative center | ||
| Republic of Bashkortostan | 142947 | 4051005 | Ufa | ||
| Kirov region | 120374 | 1272109 | Kirov | ||
| Mari El Republic | 23375 | 680380 | Yoshkar-Ola | ||
| The Republic of Mordovia | 26128 | 795504 | Saransk | ||
| Nizhny Novgorod Region | 76624 | 3214 623 | Nizhny Novgorod | ||
| Orenburg region | 123702 | 1963007 | Orenburg | ||
| Penza region | 43352 | 1318103 | Penza | ||
| Perm region | 160236 | 2610800 | Permian | ||
| Samara Region | 53565 | 3183038 | Samara | ||
| Saratov region | 101240 | 2440815 | Saratov | ||
| Republic of Tatarstan | 67847 | 3898628 | Kazan | ||
| Udmurt republic | 42061 | 1507390 | Izhevsk | ||
| Ulyanovsk region | 37181 | 1238416 | Ulyanovsk | ||
| Chuvash Republic | 18343 | 1223395 | Cheboksary | ||
Subject characteristics
Characteristics of the Samara region
Samara is a city with a rich history. There is a legend according to which its foundation was predicted in the 14th century. Moscow Metropolitan Alexy. On the way to the Golden Horde at the confluence of the Volga and Samara rivers, God's grace descended on him, and he said that “a great city will be erected here, in which piety will shine and which will not be subject to any destruction.”
The Samara fortress was built in 1586. The idea of building fortified towns between Kazan and Astrakhan was due to the need to consolidate and secure the great Volga trade route. Prince Grigory Zasekin became the head of construction and the first governor.
In 1688, Samara servicemen received a royal charter, which ordered the fortress, built in 1586, to be renamed a city. In 1730, the first coat of arms of the city was approved. In 1780, it was confirmed by a decree of Catherine II in its previous form - in the form of a shield, which depicts “a white wild goat standing on the grass in a blue field.” In 1781, Samara was elevated to the rank of a district city in the Kazan province. In 1851, Samara became the center of the province, at the same time being an important center of grain trade on the Volga.
During the Great Patriotic War, by decree of the State Defense Committee of the USSR dated October 15, 1941.
No. 801 SS “On the evacuation of the capital from Moscow” The USSR government and all diplomatic missions moved to Kuibyshev. This resolution has not been canceled to date.
Administrative-territorial division of the region: 10 urban districts and 27 municipal districts. The districts include 13 urban and 292 rural settlements.
More than three million people live in the Samara region. The bulk of the urban population are residents of Samara and Tolyatti.
The most important biological resources of the region are nature reserves and reserves, and first of all, the Samarskaya Luka National Park, Zhigulevsky State Reserve named after. I.I. Sprygina, Buzuluksky Bor reserve.
With the construction of the Volzhskaya Hydroelectric Power Station in 1957, the water of the Zhiguli Sea, which formed above the dam, became the most important hydropower resource.
1.4. Demographic situation in the Samara region
The Samara region is home to 3,178.6 thousand people, which is 2.2% of the Russian population. In terms of population, the Samara region ranks 12th among the regions of Russia and 4th among the regions of the Volga Federal District. The Samara region is a highly urbanized and densely populated region. The urban population makes up 80.4% of the total population (in the Russian Federation - 73%, in the Volga Federal District - 70.1%), population density - 59.3 people per 1 sq. km - one of the highest among the regions of the Volga region federal district (after the Chuvash Republic) - and is 2 times higher than the average value for the district.
The regional center of the Samara region is the million-plus city Samara (1,139 thousand people). On the territory of the Samara region there is a unique two-core Samara-Togliatti agglomeration.
The Samara region is characterized by a multinational population: representatives of more than 200 nationalities, ethnic groups and various self-designations live here with a significant predominance of the Russian population - 83.6% of the total.
The levels of fertility (10.1 ppm) and mortality (15.7 ppm) in the region in 2006 corresponded to the average values for the district; in the ranking of regions of the Volga Federal District for these indicators, the region was in 7th place. Despite the positive dynamics of natural reproduction processes in recent years, the region maintains a fairly high level of natural population decline: the number of deaths exceeded the number of births by 1.6 times.
Acute problems include: a high level of preventable mortality, almost every third person in the region dies at working age, an increase in the incidence of malignant neoplasms, the proportion of deaths from this cause is 12.3% of the total number of deaths.
The region accounts for 5-7% of the total migration growth in Russia.
The migration growth rate in 2006 was 23 people per 10 thousand people, which is 2 times higher than the average for the Russian Federation. In the ranking of regions of the Volga Federal District in terms of migration growth, the region took 2nd place (after the Republic of Tatarstan).
In the age structure of the population, the share of elderly citizens exceeds the share of children and adolescents (21.7 and 14.8% of the total population, respectively, as of January 1, 2007). The share of the population of working age is 63.5% of the total population, which is slightly higher than the average for the Russian Federation and the Volga Federal District. The average age of a resident of the region is gradually increasing and as of January 1, 2007 was 39.1 years.
Of the total population of the region, 54% are women, 46% are men (or 1,179 women per 1,000 men).
1.2. Natural and climatic conditions
The climate of the Samara region is characterized as moderate continental. The average annual air temperature is +3.8 degrees Celsius.
The warmest month is July. The average temperature in July is +19.3 - +21.9 degrees Celsius. The coldest month of the year is January with an average air temperature of -13.9 degrees Celsius.
Annual precipitation is low and ranges from 450 mm in the north of the region to 300 mm or less in the south. Maximum precipitation occurs in June-August.