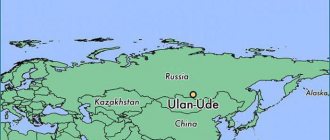
From Verkhneudinsk to the capital of Buryatia
The name of the administrative center, unusual for the Russian language, evokes associations with Central Asia or Mongolia. But that's not true. Ulan-Ude , preparing to celebrate its 350th anniversary, became the center of Buryatia in the new Russian history - in the mid-30s of the twentieth century, the city of Vehneudinsk was renamed to Red Noon - this is how today’s name of the capital of the Buryat Republic is translated.
And the story began almost three and a half centuries ago and is connected with the Cossack winter hut, which was built to collect yasak from the local Tungus population. The Buryats and Mongols did not pay taxes. A couple of decades later, a royal decree ordered the construction of the Udinsky fort on this site, marking the beginning of suburban life. In the first third of the eighteenth century, the fort was renamed the city of Verkhneudinsk. The territory begins to be built up as an urban area and becomes part of the Irkutsk governorship.
The next century was marked by the further development of the urban settlement, the construction of stone houses, a guest courtyard, the appearance of industrial and craft enterprises, and a railway station.
By the beginning of the twentieth century, about three dozen educational institutions were operating in the city, the first cars and telephone communications appeared. By the decision of the revolutionary authorities, the city becomes the capital of the newly created Far Eastern Republic, then the Baikal Governorate, and, finally, the Buryat-Mongolian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic. In the post-Soviet period, Ulan-Ude received the status of the administrative center of the Republic of Buryatia.
Crime
As for crime in Ulan-Ude, we can say that everything is relatively calm, despite some unpleasant incidents. Actually, just like in any other more or less developed city. Major incidents, shootings, bank robberies and consistent car thefts are practically non-existent. And if it does happen, then soon the culprit is found, the damage is compensated, and in the future everything is calm.
Climate and ecology of Ulan-Ude
If you like hot summers and bitter cold in winter, you will love the sharply continental climate of the capital city. There have been cases in history when in January the thermometer dropped to 54 degrees. The absolute summer maximum is 40 degrees. The sun shines almost 260 days a year, but the rainy days can be counted on one hand and there is 265 millimeters of precipitation per year. Mainly in July and August. Air humidity does not exceed 65 percent.
Despite the fact that the climate in the city is arid, it was plagued by numerous floods in the 19th century, until a large shaft was built to separate the Uda River from the urban settlement.
Earthquakes have also occurred; the capital is located in a seismically active zone due to its proximity to Lake Baikal (130 kilometers). Over the past decade, up to 150 tremors of small amplitude have been observed. They did not cause casualties or destruction.
The capital of Buryatia boasts clean air in the surrounding area; there are a large number of parks and green areas that can effectively combat the negative impact on the environment; there is a lot of motor transport in the city, and there are traffic jams on the central streets. And yet, the air is so transparent and clean that you can see mountain outlines tens of kilometers away from the city. Citizens are not afraid to drink water from the tap.
Geography[edit]
Ulan-Ude is 5,640 kilometers (3,500 mi) east of Moscow and 100 kilometers (62 mi) southeast of Lake Baikal. It lies 600 meters (2,000 ft) above sea level at the foot of the Khamar-Daban and Ulan-Burgas mountain ranges, near the confluence of the Selenga River and its tributary, the Uda, which divides the city. [10]
Hydrography[edit]
Ulan-Ude is crossed by two rivers - Selenga and Uda. The Selenga provides the largest inflow to Lake Baikal, supplying 50% of all rivers in its basin. The Selenga brings about 30 cubic kilometers (7 cubic miles) of water per year to the lake, having a great influence on the formation of water in the lake and its sanitary condition. The Selenga is home to the most valuable fish species, such as omul, Siberian sturgeon, Siberian taimen, thymallus and coregonus. [ citation needed
]
Uda is a right tributary of the Selenga River. The length of the watercourse is 467 kilometers (290 miles).
Population of Ulan-Ude
According to the rating of 1,100 Russian cities, the capital of Buryatia ranks 42nd in terms of population, 453 thousand people. Experts predict that it may become a big city in the foreseeable future. For this purpose, a municipal demographic program has been adopted, aimed at creating comfortable living conditions for the indigenous population and attracting labor resources from the countryside of the republic and other regions of Russia.
Representatives of 60 nationalities live here. Among them:
- Russians;
- Buryats;
- Mongols;
- Bashkirs;
- Evenks;
- Tajiks;
- Uzbeks;
- Belarusians;
- Ukrainians;
- Lithuanians;
Ulan-Ude is one of the few Russian cities where the male and female population is at parity. The female population predominates by a few percentage points. In recent years, more boys have been born. The population below working age is more than 20 percent. 62 percent of the capital’s residents are of working age (more than 180 thousand citizens), among them the number of people with professional education is growing. These indicators are considered the best among the regions of Siberia.
The average cost of living for the population is 8.5 thousand rubles. For pensioners, the minimum basket is set at 6.6 thousand rubles. The average salary in the economy reaches 32 thousand rubles, according to 2014 data.
The unemployment rate in 2015 is within 1.42 percent, but in the second half of the year a massive reduction is expected in budgetary organizations and in the civil service. About 2,500 people were recognized as unemployed, according to data at the beginning of 2015. There are enough vacancies in the labor market for more than three and a half thousand. The most popular specialties in the labor market are:
- car mechanic;
- mechanic;
- electrician;
- carpenter;
- tire production master;
- driver;
- mason;
- designer;
- marketer;
- administrator;
- a kindergarten teacher;
- real estate market specialist;
- insurance agent.
In 2014, the city created 4,500 new jobs in the following segments:
- wholesale and retail trade;
- services sector;
- tourism and hotel business;
- construction;
- cargo transportation.
Twin cities - sister cities[edit]
See also: List of sister cities and sister cities in Russia
Ulan-Ude is twinned with: [20]
- Anyang, South Korea
- Berkeley, USA [21]
- Changchun, China
- Chita, Russia
- Darkhan, Mongolia
- Donetsk, Ukraine
- Elista, Russia
- Erdenet, Mongolia
- Erenhot, China
- Grozny, Russia
- Haeju, North Korea
- Hohhot, China
- Hulunbuir, China
- Lanzhou, China
- Manzhouli, China
- Rumoi, Japan
- Taipei, Taiwan
- Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
- Ulanqab, China
- Yalta, Ukraine
- Yamagata, Japan
- Yongwol County, South Korea
Panoramic view of Ulan-Ude
Budget and investments
The capital's budget revenues in 2015 will amount to 3.6 billion rubles. The third part of the expenses is aimed at developing education and preparing for the celebration of the 350th anniversary of the city. The budget deficit is planned to be kept within 10 percent of revenues of 300 million rubles. Interestingly, the city fathers plan to achieve a budget surplus by 2016. Primarily due to investment projects, both public and private. Since 2014, more than fifty promising projects have been implemented in the republic with a total capital investment of up to 250 billion rubles. The largest of them:
- construction of regional roads with a length of 40 kilometers;
- reconstruction of 200 kilometers of federal highways;
- reconstruction of 17 bridges with the construction of 9 entrances;
- construction of three autotourist complexes;
- construction of infrastructure for a tourist and recreational park with a complex of buildings in Podlemorye;
- fortification and hydraulic structures on the banks of the Selenga River;
- landscaping of urban areas and new buildings in the steppe zone;
- construction of production facilities for processing solid waste;
- expansion of the capital's airport runway;
- complex development of microdistricts of the capital in the southern direction.
Such large investments are aimed at improving the demographic situation in the region and increasing the living comfort of citizens. In the long term, it is calculated that the number of capital residents will double by 2027.
Districts and new buildings
There has been a noticeable acceleration in housing construction. If in 2006 less than one hundred thousand square meters were commissioned in the region, then in 2014 there were 207 thousand square meters or 2,400 apartments. For 2015, the government of the republic has set an ambitious goal of putting into operation at least 3,500 comfortable apartments. Massive construction is carried out mainly in the capital of the republic, where residents from rural settlements and other Russian regions are moving.
Immigrants are attracted by the number of jobs with decent salaries, the relative cheapness of life in comparison with Irkutsk, Chita and Novosibirsk, and affordable housing. The average price per square meter in the city does not exceed 40 thousand rubles. The average citizen's salary is enough to purchase one square meter of housing per month.
The capital's development policy has changed from spot compacting to high-rise blocks. In 2014, 17 hectares of city land were allocated for complex development for the implementation of the Housing for Russian Family program. As part of the state program, more than one hundred thousand square meters will be built at a price not exceeding 30 thousand rubles.
The city administration is putting up for auction land plots for individual housing construction: eight acres will cost new residents half a million rubles.
In the Oktyabrsky district, the following are attractive to citizens:
- Residential complex Nikolsky, consisting of high-rise residential buildings with underground parking. The complex is located near the center, near shopping centers, schools, kindergartens, and a clinic. At the construction stage, and it will be put into operation in 2016, the cost per square meter is negligible 33 thousand rubles.
- Residential complex Angara 2 offers apartments in five 16-story towers. Within walking distance of a market, school, clinic, university, kindergarten. There is a children's playground on the roof of the underground parking lot. A square meter of housing will cost 42 thousand rubles. All houses have been put into operation.
- Residential complex Favorite is located in the very center. You can get to any area of the city by public transport without transfers. A three-room apartment with an area of over 80 square meters in a brick house costs 3.2 million rubles.
- The Flagman residential complex is surrounded by the sights of the Mother of Buryatia monument, Selingovsky Bridge, Megatitan and Eldorado shopping centers. One-room apartments up to 40 square meters are valued at 1.7 million rubles.
There is no comprehensive residential development underway in the Zheleznodorozhny district of the capital, but in new buildings on Oktyabrskaya Street you will be offered many apartments starting from 45 thousand rubles. A plot of 6 acres for individual housing construction is available for 200 thousand rubles.
In the cottage village of Lesnaya Polyana (Sovetsky district), you can purchase real estate with an area of 150 square meters for only 1 million 150 thousand rubles under hot offers. A house with a rough finish and a plot of 8 acres in the same area will cost a new resident 1.35 million rubles. An apartment near the airport with an area of 33 square meters is being put up for auction for 1.2 million rubles.
Surprisingly, secondary housing in the capital is cheaper than new buildings. You can find an option from 20 thousand per square meter of housing.
Links[edit]
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Ulan-Ude . |
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b in "Baikal24".
- ^ abc Federal State Statistics Service (2011). “All-Russian Population Census 2010. Volume 1" [All-Russian Population Census 2010, vol. 1]. All-Russian Population Census 2010 [All-Russian Population Census 2010]
. Federal State Statistics Service. - "26. The size of the permanent population of the Russian Federation by municipalities as of January 1, 2022". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2022.
- ^ abc Resolution No. 431
- ^ abc Law No. 985-III
- "On the Calculation of Time". Official Internet portal of legal information
. June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2022. - Post office. Information and computing center of OASU RPO. ( Post office
).
Search for postal service objects ( postal Search for objects
) (in Russian) - ^ ab Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). “The population of Russia, the constituent entities of the Russian Federation as part of federal districts, urban settlements, settlements, settlements is 3 thousand or more people” [Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal districts, districts Urban settlements, rural settlements - administrative centers and rural settlements with a population of over 3,000] (XLS). All-Russian Population Census 2002
. - Jump up
↑ Chisholm, Hugh, ed.
(1911). "Verkhne-Udinsk". Encyclopedia Britannica
.
27
(11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. item 1023. - transsibirskaya.com
- britannica.com
- Bisher, Jamie (June 2005). White Terror: Cossack commanders of the Trans-Siberian Railway
. pp. 302–03. ISBN 9781135765958. - “Historical prerequisites for the formation of the modern ethnic structure of Ulan-Ude”. ethonet.ru. Archived from the original on February 13, 2012. Retrieved April 17, 2022.
- “All-Union Population Census of 1989. The actual population of the union and autonomous republics, autonomous regions and districts, territories, negative phenomena, urban settlements and rural areas. Russian Census 2010” (PDF). July 27, 2022
- ^ a b Monument to V.I. Lenin (in Russian). Monulent.ru. Retrieved April 17, 2022.
- "Climate of Ulan-Ude". Pogoda.ru.net. Retrieved May 15, 2022.
- "ULAN-UDE / MUKHINO 1961–1990". NOAA. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- "Twin Cities". ulan-ude-eg.ru
(in Russian). Ulan-Ude. Retrieved February 1, 2022. - "Twin Cities - City of Berkeley, California". www.cityofberkeley.info
. Retrieved September 25, 2022.
Sources [edit]
- Government of the Republic of Buryatia. Resolution No. 431 of November 18, 2009 “On the register of administrative-territorial units and settlements of the Republic of Buryatia,” as amended. Resolution No. 573 of November 13, 2015 “On amendments to the Decree of settlements of the Republic of Buryatia dated November 18, 2009 No. 431” On the register of administrative-territorial and settlements of the Republic of Buryatia “”. Entered into force on November 18, 2009. Published: “Buryatia”, No. 216, Official Gazette No. 120, November 21, 2009 (Government of the Republic of Buryatia. Resolution No. 431 of November 18, 2009 “ On the register of administrative-territorial units and populated areas points of the Republic of Buryatia"
as amended by Resolution No. 573 of November 13, 2015.
On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Republic of Buryatia of November 18, 2009 No. 431 "On the register of administrative-territorial units and settlements of the Republic of Buryatia"
. Valid from November 18, 2009 G.). - People's Khural of the Republic of Buryatia. Law No. 985-III of December 31, 2004 “On the establishment of boundaries, formation and granting the status of municipalities in Buryatia,” as amended. Law No. 1411-V of October 14, 2015 “On Amendments to the Law of the Republic of Buryatia” On the establishment of boundaries, formation and granting the status of municipalities in Buryatia “”. Came into force on the date of official publication. Published: “Buryatia”, No. 1, Official Gazette No. 1, January 12, 2005 (People's Khural of the Republic of Buryatia. Law No. 985-III of December 31, 2004 “ On establishing boundaries, creating and granting status to municipalities in the Republic of Buryatia "
, as amended by Law No. 1411-V of December 31, 2004. October 14, 2015
On amendments to the Law of the Republic of Buryatia “On establishing boundaries, creating and granting status to municipalities in the Republic of Buryatia
.” Valid from the date of official publication .).
Sights and culture
The main attraction of the capital is a bronze monument to the leader of the world proletariat, an almost eight-meter tall head of Lenin cast in bronze, rising on a high, more than six meters, granite pedestal. Its production took 42 tons of non-ferrous metal.
In the vicinity of the city, the main shrine of Russian Buddhists was erected, the Ivolginsky Datsan Khambyn Sume. Thousands of pilgrims and tourists come here to explore the unique temple complex. Guests can stay at a hotel on the territory of the monastery.
The Rinpoche Bagsha Buddhist Center houses the largest gilded Buddha statue.
The ethnographic museum, whose holdings occupy more than 40 hectares, introduces guests to the history of the peoples of Transbaikalia. Thousands of copies telling about the historical development of Buryatia are collected in one open-air place.
Walking along Lenin Street, the pedestrian part of which was named the Buryat Arbat, you will see the symbolic coat of arms of the republic - a marble sculpture with bronze snakes, the Rod of the god of trade Mercury and a cornucopia.
The sculptural composition Beauty of the Angara is installed near the Opera and Ballet Theater. The dance composition is dedicated to the outstanding ballet masters of Buryatia.
On the central street of Kuibyshev there is the Trinity Church of the late 18th century, the shopping arcade of the merchant Kurbatov. Here you can walk around the estate of the tradesman Burlakov.
The largest museums, theaters, and exhibition halls of the republic are concentrated in the capital. The national song and dance theater Baikal successfully tours around the world.
Guests of the city enjoy visiting numerous museums:
- Museum of the History of Buryatia, where the richest collection of Buddhist religious objects is collected;
- Museum of Nature of the Republic;
- Art Museum;
- Museum of Applied Arts.
Education
At the beginning of the 19th century, the population of the territory was not literate. There was only one public school, where they learned crafts and school basics. Today, a quarter of the capital's population are students of secondary specialized and higher educational institutions. There are over 80 secondary schools and the same number of kindergartens in the city. By 2016, according to the administration's plans, there will be no queues in preschool institutions in the city. New kindergartens are being built in housing complexes in the south-eastern part of the city.
More than 35 thousand young people study in 17 universities of the republic: 5 state universities and 12 branches. Specialists are trained:
- Buryat State University;
- East Siberian State University of Technology and Management;
- Agricultural Academy;
- Institute of Public Administration
- Agricultural Academy
- Institute of Railway Transport.
Young people receive secondary vocational education in 17 technical schools, colleges and schools.
The city has the Buryat Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, industry research institutes, and a fruit and berry experimental agricultural station.
Healthcare
In addition to a developed network of clinics and hospitals, a unique state Center for Oriental Medicine with several buildings has been created in the city. The following services are provided here:
- bioenergetic diagnostics;
- biochemical studies;
- consultations with narrow specialists;
- treatment using Tibetan medicine methods;
- rehabilitation.
There are a number of private medical centers and offices in the capital of the republic. The Center for Oriental Medicine also provides a number of paid services.