Shadrinsk is a city geographically located on West Siberian Plain. Occupies the position of the center of the Trans-Ural region in many areas. Shadrinsk on the map of Russia is part of the Kurgan region.
Shadrinsk assumes the role of the historical center of the Kurgan region. A large number of historical buildings have been preserved on the territory of the city, which are protected by the state as a cultural heritage.
The city was founded in 1662. It is located on the left bank of the Iset River.
City `s history
The population of Shadrinsk is now comparable to the number of people who lived in the city in the early 70s of the last century. The main outflow of local residents began in the 2000s and continues to this day.
The city of Shadrinsk itself was founded in the 17th century. This was done by Russian explorers who developed the Far Eastern and Siberian lands. The founder of the local settlement is considered to be Yuri Malechkin, who petitioned Tobolsk to be allowed to build a settlement and a fort in this place. By 1686, Shadrinskaya Sloboda was the largest in Western Siberia. There were more than 130 peasant households, where dragoons and Cossacks lived.
Shadrinsk on the map of Russia: geography, nature and climate
Population of Poland
The total area of the city of Shadrinsk is small, only 173.66 km2. The city has the status of regional subordination. Shadrinsk is one of three cities that are part of the main merchant cities of the Urals.
The distance from Yekaterinburg is about 230 km. The satellite map of Shadrinsk well illustrates the area in which the city is located - forest-steppe.
The time zone is focused on Yekaterinburg and in relation to Moscow has a difference of +2 hours.
Shadrinsk takes on a cold temperate climate. The average temperature throughout the year is 2 degrees. The city is characterized by high precipitation. The driest period in the city is also accompanied by precipitation.
July is considered the warmest month of the year; in this month the air warms up to 20 degrees. The coldest month is January, at which time the air temperature drops to -20 degrees. March is one of the driest months, with little rainfall at this time.
Shadrinsk becomes a city
Shadrinsk received city status in 1712. In 1733, a major fire almost destroyed it. The recovery took a long time.
In 1774, during the uprising of Emelyan Pugachev, the city refused to join the rebels. Soon reinforcements arrived from Siberia, the tsarist troops went on the offensive and defeated the rebels. Shadrinsk received the status of a district town in 1781. At the same time, the settlement received its own coat of arms - it depicts a marten running across a silver field.
In 1842-1843, Shadrinsk once again became the center from which the suppression of the peasant uprising began, which went down in history as the “potato riot.”
Economy
The economic situation in the city is determined mainly by manufacturing industries; their share in the turnover of large and medium-sized enterprises is more than 95%. The city's largest enterprises include:
- OJSC Shadrinsky Automotive Aggregate Plant is an enterprise producing automobile radiators, heating radiators, hydraulic jacks, and charge air coolers.
- OJSC Shadrinsky Electrode Plant is an enterprise producing electrodes for welding carbon, low-alloy, high-alloy and heat-resistant steels. In 1992, as a result of privatization, the workshop acquired the status of the Shadrinsk Electrode Plant.
- Shadrinsky Metal Structures Plant LLC.
- CJSC Shadrinsk Plant of Reinforced Concrete Products and Metal Structures.
- OJSC Shadrinsky Plant of Enclosing Structures.
- OJSC Shadrinsky Telephone Plant is an enterprise producing HF communication equipment.
- Delta Technology LLC is a mold production company.
- Tekhnokeramika LLC is an enterprise producing proppants for the oil industry.
- Liteishchik LLC is an enterprise producing non-ferrous and cast iron castings.
- Shadrinsk Diesel Locomotive and Car Repair Association LLC is an enterprise engaged in the overhaul of railway equipment.
- Shadrinsky Polymer Bag Packaging Plant LLC is an enterprise producing polypropylene fabric, polypropylene bags and soft containers.
- CJSC Shadrinsk Furniture Factory is an enterprise producing cabinet furniture for home and office.
- LLC "Trans-Ural Textile Bag Factory" is an enterprise producing travel and sports bags.
- Among the largest food industry enterprises: Shadrinsky Dairy and Canning Plant (dairy products), Shadrinsky Brewery LLC (vodka and wine), Slakon JSC (confectionery products), Shadrinsky Bread Products Plant JSC (cereals and flour) and other.
The average monthly salary of one employee of large and medium-sized enterprises in January 2012 was 14,843 rubles.
There are branches of Russian banks in the city: "Agropromcredit", "VUZ Bank", "Bank Let's Go", "Bank Kurgan", "Ring of the Urals", "VTB 24", "Rosgosstrakh Bank", "Rosselkhozbank", "Sberbank of Russia", "Uraltransbank", "Khanty-Mansiysk Bank", "Home Credit and Finance Bank", "East Express Bank", "Mosoblbank".
The city has GSM, 3G and 4G cellular operators: Beeline, MegaFon, MTS, Tele2, Motiv and Yota. Internet access is provided by the providers Courier Plus, Rostelecom, and SHADR.RU.
Development at the beginning of the 20th century
The population of Shadrinsk began to increase at the beginning of the 20th century. The emergence of a large number of industrial production and enterprises played a special role in this. In particular, the spinning and weaving factory of the Butakov brothers, the agricultural workshop of Molodtsov.
In the first decade of the last century, a real school, a women's gymnasium, and a teachers' seminary were opened here. By 1917, it was a fairly large county town; the population of Shadrinsk at that time was 17 thousand people.
During the Civil War, power here changed several times. At the very beginning of 1918, the Bolsheviks occupied it, but by the summer they were knocked out by Czech troops. In August, a model of a monument to the victims of the Bolshevik execution was even installed. Red troops returned Soviet power by August 1919.
In 1925, a distillery opened in the city, which existed until recently, only going bankrupt in 2006. Since 1933, mechanical and iron foundries have been operating in the city.
During the Great Patriotic War, enterprises were created in Shadrinsk on the basis of evacuated factories. In the future, automobile assembly plants, telephone plants, tobacco and clothing factories will appear here.
The telephone plant produces products to support space flights. In 1975, cosmonaut Yuri Artyukhin arrived in Shadrinsk and presented the teams with gratitude from the Council of Ministers for producing high-quality products.
Healthcare
Today there are more than 20 medical institutions in Shadrinsk. Among them: Shadrinsk Emergency Hospital, Shadrinsk Polyclinic, Shadrinsk Children's Hospital, Shadrinsk Central District Hospital, Shadrinsk Regional Tuberculosis Dispensary, Shadrinsk Regional Psychoneurological Dispensary, Shadrinsk Regional Drug Dispensary, Shadrinsk Regional Blood Transfusion Station, Dermatovenerological Dispensary, medical doctor45.ru , Shadrinsk city maternity hospital, Clinic at the station. Shadrinsk (JSC Russian Railways), Shadrinsk dental clinic, private dentistry “Spectra” and others.
Modern reality
Since the early 90s, after the collapse of the Soviet Union, the situation of many large industrial enterprises has deteriorated significantly. Plants and factories are closing or moving to part-time work.
In 1996, the Poligrafmash plant significantly reduced its production capacity, on the basis of which a new enterprise, Delta-Technology, was formed. In 2003, the Volodarsky garment factory, which had existed in the city since 1941, closed.
Soviet time
In 1919, a city museum with a scientific repository and a Komsomol organization were opened, and industrial, textile and food production was improved.
In the late 1920s - early 1930s, the Railway, Automechanical, Accounting and Financial, Agricultural and Economic Colleges and the Pedagogical Institute, a meat processing plant, a distillery, a shoe and felt factory, a furniture factory appeared, and an airfield was built.
During the Second World War, large enterprises of union significance were transported to the city:
- plant named after Likhachev (Stalin plant - SHAAZ)
- metal rolling plant (future ShZRT)
- Printing plant (SHZPM)
- Moscow Radio Plant (SHTZ) and many others
.
Part of the Pedagogical Institute is being transferred to Kurgan, and KSPI will soon be formed on its basis. Some funds of the city archive are evacuated to Kurgan, Omsk, Tobolsk, and later they will be transferred to Yekaterinburg and the State Archive.
After the war, the Pedagogical Institute, the Music and Art School named after. Bronnikova. A Dairy Canning and Poultry Plant, a House-Building Plant and a Mobile Plant are being built.
At the end of 1960, rapid construction of apartment buildings (the so-called Brezhnevok), shops, bus stops began, the urban area was improved - squares and parks were laid out, gardening associations appeared en masse.
After perestroika, unfortunately, as throughout the country, there was stagnation in all spheres of life: enterprises were closed, kindergartens were transferred to business, prices rose.
State Drama Theatre.
However, many initiatives of past Soviet years are now beginning to be revived. The city of Shadrinsk is becoming prettier before our eyes and is still rightfully called the cultural and sports capital of the Trans-Urals.
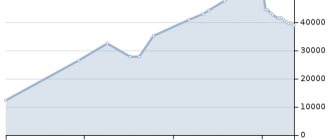
Population dynamics
The first data on the population of the city of Shadrinsk dates back to 1793. At that time, 817 people were registered here. Already at the beginning of the 19th century, the population of Shadrinsk increased significantly - to more than two thousand inhabitants.
In 1825 there were already two and a half thousand local residents. And in 1835, the population of Shadrinsk exceeded three thousand people. In 1861, the year of the abolition of serfdom in the country, almost 6 thousand people lived in this city.
In 1897, the number of inhabitants exceeded the psychological mark of 10,000.
How to get
You can get to Shadrinsk in several ways:
- By train or train;
- By intercity bus.
- By car.
There are direct trains from several large cities to Shadrinsk. It is possible to get there without transfers from cities such as:—Moscow;
- -Ekaterinburg;
- -Mound;
- -Kamensk-Uralsky;
- -Kazan;
- -Petropavlovsk;
- -Sarapul.
Intercity bus service to Shadrinsk runs from: Kurgan;
- -Tobolsk;
- -Khanty-Mansiysk;
- -Chelyabinsk;
- -Tyumen and others.
What is the route to Shadrinsk along the federal highway? You can get there by car along the following roads:
- P330 “Shadrinsk - Chelyabinsk”;
- P354 "Ekaterinburg - Kurgan".
Where is Shadrinsk on the map?
On the map of Russia, the city is located in the Kurgan region, on the West Siberian Plain, east of the Ural Mountains. Shadrinsk coordinates: 56.08° north latitude and 63.63° east longitude.
Shadrinsk in our time continues to be an industrial center. In addition to its interesting history, the city has a rich cultural heritage. You can admire the architectural monuments of the 19th century, the St. Nicholas Church of the 18th century, and many valuable historical exhibits are collected in the local history museum.
The city of Shadrinsk is worth visiting for those who are interested in the past of their native land, for those who like to discover new, historically valuable places.
Population in the 20th century
After the advent of Soviet power, the number of residents in Shadrinsk gradually increased. If in 1923 there were 18 thousand 600 people here, then already in 1939 there were more than 31 thousand Shadri residents. After the war, growth continued - in 1948, more than 50 thousand people already lived here.
True, after this some industrial enterprises are removed from Shadrinsk, and the number of residents drops significantly because of this. By 1950, about 35 thousand people remained. People began returning to the city to which our article is dedicated in the late 50s. And at a fast pace. During perestroika, more than 80 thousand people registered here.
It is noteworthy that in the 90s, unlike most small cities in Russia, the population here was growing, albeit at a slow pace. Shadrinsk managed to achieve its highest figures in 1997; according to statistics, 88 and a half thousand people live here.
In the 2000s, many Shadrinsk enterprises found themselves in crisis. Every year there are fewer and fewer residents. At the moment, a little more than 75 and a half thousand people live here. Now you know how many people are in Shadrinsk.
mass media
Main article: Shadrinsk media
Television has been broadcast in the city and region since 1963. The broadcast takes place through 2 television towers, in the northern part of the city, along Karl Liebknecht Street (the mast is not currently in use) and RTPS in the northern part of the city, Avtomobilistov Street, 1″b (mast 245.9 m). Before the collapse of the Union, 4 union channels and one regional channel were broadcast in the city. Since 1990, a city channel appeared. Currently, the main federal channels are received (20 channels).
Radio appeared in Shadrinsk in 1920-1930. From December 31, 2004 to 2011, the Shadrinsk information and music radio station operated.
“Shadrinsky Rabochiy” was renamed “Shadrinskaya Nov” in 1988, and in 1990 - “Iset”.
- "Your Benefit" has been published since 1999 and currently appears on Tuesdays and Fridays.
- "Avtoagregat" is the newspaper of the Shadrinsky Autoagregat. Published weekly since 1943.
- “Dela and People” is a newspaper published monthly by the Shadrinsk enterprise “Technoceramics” since 2008.
- “Business Shadrinsk” is a weekly newsletter. Published since 1999.
- “Lifestyle” is a newspaper published by the Shadrinsk city consumer society “Ural” since 2002.
Ongoing editions
Since 1994, the local history almanac “Shadrin Antiquity” has been published in the city (https://nlr.ru/kraeved_periodika/edition/123). By the beginning of 2021, a total of 28 issues were published, where more than 500 articles on the history of Shadrinsk were published.
Unemployment rate
Due to the large number of industrial enterprises, the unemployment rate in Shadrinsk remains one of the lowest in the entire Kurgan region. On average, about 0.9 percent of the total economically active population. In physical figures this is less than 400 people.
The credit for this goes to the employment center of Shadrinsk, which is located at Sverdlova Street, building 58. You need to get there by public transport to the “Cosmos” or “Spartak” stop.
At the same time, the number of vacancies in the Shadrinsk employment center is approximately twice the number of unemployed. The labor market is experiencing a shortage of cooks, pastry chefs, technologists, waiters, kindergarten teachers and school teachers. The situation is especially acute in social and medical institutions that require doctors, junior and nursing staff.
Transport
Population of Taganrog
Main article: Transport of Shadrinsk
Shadrinsk is a major transport hub in the north-west of the region and the second in the region after Kurgan. Two federal highways P354 and P330 pass through the city, as well as two regional highways P329 and Shadrinsk - Shumikha.
On the territory of Shadrinsk there is a passenger station Shadrinsk, where the station operates. Shadrinsk station is part of the Kurgan branch of the South Ural Railway, a branch of Russian Railways OJSC. The station is located on the Kurgan-Kamensk-Uralsky railway line. By train from Shadrinsk you can get to Moscow, Petropavlovsk, Almaty, Bishkek, Tashkent and other cities. By electric train from Shadrinsk you can get to Kurgan, Yekaterinburg and Kamensk-Uralsky. The branded passenger train “Zauralye” Kurgan - Moscow runs through Shadrinsk.
The current building of the railway station was built in December 1973: one wing of it was the railway station itself, and the second wing was the bus station. The unified bus and railway station functioned until 2010, when, at the request of the formal owner (Russian Railways), the bus station was evicted from the building on Ordzhonikidze Street, 13a (the area adjacent to the Shadrinsky Automotive Aggregate Plant). In 2022, the bus station returned to the premises of the railway station; buses from Shadrinsk to Kurgan, Yekaterinburg, Tyumen, Chelyabinsk, Tobolsk, Khanty-Mansiysk and other cities depart from the station square.
The nearest international airport is in Koltsovo (near Yekaterinburg, 233 km). The nearest regional airport is in Kurgan (140 km). On the southern outskirts of Shadrinsk there was an airfield that served as a training center for navigators at the Shadrinsk Military Aviation School of Navigators. After its disbandment in 1960, the airfield became a center for training navigators at the Chelyabinsk Military Aviation Institute of Navigators. Three squadrons of Tu-124Sh and Tu-134Sh aircraft were based there.
City public transport
See also: Shadrinsky bus
The main public transport in the city of Shadrinsk is the bus. Every day, to transport passengers on 34 routes, buses of the GAZelle, PAZ and Ford Transit brands leave from Shadravto LLC and Avtotrans LLC, as well as from private carriers. The main routes pass along the main streets of Shadrinsk.
The city also has developed taxi networks that transport passengers in passenger cars of domestic and foreign production.
Intercity and suburban communication
See also: Shadrinsk (station)
For intercity communication with the city, buses departing from the Shadrinsky bus station are used. Transportation is carried out by Shadravto LLC and Avtotrans LLC, as well as by other private carriers. Routes intended for suburban traffic depart to the Shadrinsky district.
Pre-revolutionary time
The city of Shadrinsk is one of the oldest merchant cities in the Urals.
Trade on the river bank Iseti. Con. XIX century
It begins its history in 1644, when on the site of the future settlement, Cossack Efim Shadrin, a native of the Russian North, founded a settlement where men from the surrounding villages fished and hunted.
In 1662, by order of the Tobolsk administration, a settlement appeared on the site of the settlement. Yuri Nikiforov Malechkin fulfilled the sovereign’s task by recruiting free people from other regions, primarily from Arkhangelsk, Vologda, Vyatka.
Torgovaya Street (Komsomolskaya). Beginning XX century
A fortified wall surrounded the settlement in a matter of months.
Gradually the population grew, and in 1712 the settlement became a city, and the first city manager, Prince Vasily Meshchersky, was appointed.
The 18th century was fertile for extraordinary historical events: riots, uprisings, changes of power - the city survived everything, but the fires became a greater disaster than the Pugachevites.
Since 1777, the city has been building stone buildings: the first was the Transfiguration Cathedral.
View of the Transfiguration Cathedral. Con. XIX century
In 1781, the city received a coat of arms and became the center of the county of the same name. At the end of the century, the first city school appeared.
Various factories and handicraft workshops operated in Shadrinsk.
In the 19th century, these were a porcelain and earthenware factory, a Poklevsky-Kozell distillery, a soap factory, a fulling factory, a lard distillery and a distillery.
Large fairs were held here, including Krestovsko-Ivanovskaya, the second most important in the empire.
With the advent of the zemstvo in Shadrinsk, the City Duma developed, shops, large retail establishments, a zemstvo hospital, banks, a city garden, a weather station, an experimental fruit and vegetable station and much more were built.
In 1896, the city theater received a separate building.
View of the southern part of the city. Con. XIX century
By the end of the century, there were 6 churches and one cathedral in the city.
By the beginning of the 20th century, more than 16 thousand people lived in the city (for example, in Kurgan 9.5 thousand, Yekaterinburg 37 thousand, Chelyabinsk 19 thousand, Perm 45 thousand people).
In 1912-1913, the Shadrinsk-Sinarskaya railway came into operation. In general, the city has entered a century of rapid construction. The city newspaper “Iset” is published.
Kurgan Regional Duma
- home
- Kurgan region
- Districts, districts and cities
- Shadrinsk city
Brief information
the city of Shadrinsk was founded in 1662. The territory of the city is 0.2 thousand square meters. km. Population: 74,652 people (as of 01/01/2020) National composition: Russians - 94.4%, Tatars - 2%, Ukrainians - 1% Included in the Shadrinsky No. 1 electoral district, Shadrinsky No. 2 electoral district. City administration:
City Duma:
Deputies of the Regional Duma elected in a single-mandate constituency:
Deputies of the Regional Duma elected from a single electoral district:
General information
The city of Shadrinsk was founded in the 17th century, when Russian explorers began to develop open Siberian and Far Eastern lands. Under the cover of the walls of the Shadrinsky fort, the banks of the Iset River were settled by peasants from the northern and other provinces of Russia, who were looking for a better life beyond the Urals. Since 1712, Shadrinskaya Sloboda was renamed the city of Tobolsk district. It quickly became not only an administrative, but also a major economic center of the Southern Trans-Urals.
Such names of our fellow countrymen are associated with Shadrinsk as the artist, professor of painting Fyodor Andreevich Bronnikov (1827-1902), sculptor Ivan Dmitrievich Ivanov - Shadr (1887-1941), local historian Vladimir Pavlovich Biryukov (1888-1971).
As of January 1, 2020, the permanent population of Shadrinsk is 74,652 people.
In 2022, 23 preschool educational organizations, 15 schools and branches, and 8 additional education organizations operate on its territory in 2022. In the field of vocational education, there are two secondary education organizations (Shadrinsk Polytechnic College, Shadrinsk College of Physical Culture and Health, Shadrinsk Financial and Economic College - a branch of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Shadrinsk branch of the Kurgan State Budgetary Educational Institution basic medical college").
The healthcare system has 4 hospitals and 4 clinics.
On the territory of the city there are 13 cultural and art institutions, including 4 clubs and houses of culture, 7 libraries.
Today Shadrinsk is the second most important city in the region. 131 enterprises and organizations are engaged in industrial activities. The main enterprises located in the city: Shadrinsky Automotive Plant JSC (heaters and pre-heaters for cars, oil and water radiators, pipe packages and frames), Tekhnokeramika LLC (produce proppants and other technical ceramic products for oil production), JSC Shadrinsky Telephone Plant", Dairy Plant "Shadrinsky" - a branch of OJSC "Unimilk Company" (whole milk products, canned milk). Small businesses are developing rapidly.
On the territory of the city, 9 mineral deposits have been explored and used, including brick and tile raw materials - 3,159 thousand cubic meters, underground mineral waters - 481 cubic meters per day, drinking underground water - 1,970 cubic meters per day .
The number of small and medium-sized businesses is 2,345 units, including 1,760 individuals carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity (individual entrepreneurs and heads of peasant (farm) farms).
There are 7 hotels for city guests.
For the purpose of socio-economic development of the territory, 21 investment sites have been created, 26 investment projects are being implemented.
In the city of Shadrinsk, a map of investment sites has been developed, according to which land plots are allocated for the location of production and industrial facilities, as well as land for agricultural use and housing construction.
Date modified: 06/28/2021 12:22