Live in a satellite city and work in Yekaterinburg. Is this a good option?
Yekaterinburg is gradually turning into a large business and noisy metropolis. Increasingly, people are starting to think about moving to live in a quiet and peaceful suburb.
Yekaterinburg has 4 satellite cities:
- Berezovsky;
- Upper Pyshma;
- Aramil;
- Sredneuralsk
In the article, consider all the pros and cons of the idea itself and each satellite city.
Current statistics
The Sverdlovsk region is a subject of the Russian Federation, part of the Ural Federal District. The capital is Yekaterinburg, from whose former name “Sverdlovsk” the name of the region comes. The administrative center of the region was founded back in 1723.
It was this year that the metallurgical plant on the Iset River began operating. As of January 2022, according to Rosstat, 4,310,681 people live in the Sverdlovsk region. Population density – 22.18 people per square meter. km.
Lesnoy is a large city located in a closed area
Surprisingly, the third largest city of Lesnoy with an area of 360 km² is only on the 13th place in the list of the largest cities by the number of inhabitants. This is explained simply: the formation is a closed territory, since the Elektrokhimpribor plant, which works with uranium, is located here. The factory and then the settlement were built by Gulag prisoners. In the first years of its existence, it was called Sverdlovsk-45: only in 1994 the name was renamed.
In this regard, there are no significant attractions in Lesnoy, but the infrastructure for local residents is well developed. There are about 500 companies in various segments of the economy, as well as 3 universities, among which there is one that corresponds to the profile of the city - a branch of the Scientific Research Nuclear University MEPhI.
Data by year
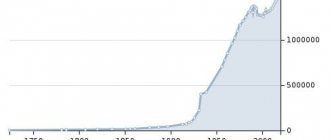
If we compare the data on the population of the Sverdlovsk region by year, we can see that since 1959 the number of residents has changed relatively little. So, in the named year, just over 4 million people lived in the region, whereas in 1970 more than 4 million 300 thousand people already lived here. The maximum number of inhabitants was recorded between 1979 and 1994. starting from 1995 the number of people begins to gradually decrease:
- 1995 – 4678975;
- 1996 – 4660022;
- 1997 – 4641304;
- 1998 – 4625057;
- 1999 – 4607587;
- 2000 – 4577515;
- 2001 – 4545942.
As you can see, Perestroika and the 1990s. did not have a significant impact on the population. The minimum number of residents was recorded in 2011 – 4,297,227 people. The current demographic situation can be compared with 1970, as discussed above, although in terms of the number of newborns, 2022 is still inferior to 1970. In 1970, 14.5 babies were born per 1000 people, and in 2022, slightly more than 13. By comparison, in 1979, almost 17 babies were born. The decreased birth rate is observed against the background of increasing mortality. If in 1970 about 8.4 people died per 1000 thousand people, then in 2022 this figure almost doubled.
Important ! Most people died between 2000 and 2004. In 2003, there were 17.3 deaths per 1000 people with 10.4 newborns.
History of the Sverdlovsk region in the twentieth century
When the Soviet government came to power, industry began to rapidly develop in the region. During the period from 1925 to 1939, the population of the Sverdlovsk region increased by almost 900,000 people.
During the Great Patriotic War, the number of residents changed greatly. Enterprises were evacuated to Nizhny Tagil, Asbest, Yekaterinburg (then called Sverdlovsk), and workers arrived along with factories. Between 1939 and 1959, the population grew at an annual rate of 2.7 percent. This was five times the national average.
Until the late 1950s, there was the greatest population growth. New residents arrived in large numbers until the late 1960s, after which the dynamics remained almost unchanged. Less money was invested in the region's economy than usual. Forest resources began to be depleted, and many minerals were exhausted. In addition, the birth rate began to decline. This was because women were more involved in production than before. In addition, developed culture and education have led to greater demands from the population regarding the standard of living.
When the Soviet Union collapsed, the outflow of the population of the Sverdlovsk region to other regions of Russia began. It continues to this day. Villages are emptying and dying out.
Cities
In the Sverdlovsk region there are 47 large cities, as well as 27 urban-type settlements with a population of 2 to 15 thousand people. The largest:
- Ekaterinburg. Almost 1.5 million people live in this city. Founded in 1723 and named in honor of Catherine the First. It received city status already under Catherine the Great in 1781. At the beginning of the last century, Ekaterinburg became the center of the revolutionary movement of the Urals. During the Second World War, the largest heavy engineering plant was located in Yekaterinburg. Today it is the fourth largest city in Russia, the country's largest transport and logistics hub and administrative center. In 2022, Yekaterinburg received the title of city of labor valor. The Yekaterinburg agglomeration is home to over 2.2 million people with a population density of more than 3 thousand people per square meter. km.
- Nizhny Tagil. Founded in 1722. Now more than 349 thousand people live here with a density of 1173.25 people per square meter. km. The city is multinational, Russians, Ukrainians, Tatars live here, there are citizens of Belarus and Azerbaijan. Compared to 1897, the city's population has increased 10 times. At the end of the 19th century, barely more than 30 thousand people lived here. The maximum number of inhabitants was reached in 1989 and 1991. During this period, according to statistical data, about 439,000 people regularly lived in the city. Approximately the same number of residents lived in Nizhny Tagil in 1994, but in 1995 and in subsequent years the figure changed downward. Residents leave for capital cities, die, and fewer children are born. It is interesting that among the 1115 largest cities in Russia, Nizhny Tagil is given 54th place.
- Kamensk-Uralsky. A city in the Middle Urals with a population of 166,086 people with a density of 1152.73 people per square meter. km. Founded in 1682, for some time, until 1699, it remained a territory. Modern Kamensk-Uralsk consists of 2 districts, is the third largest city in the Sverdlovsk region in terms of population and density, and the tenth in terms of the number of railway transport hubs passing through its territory. More than 174 thousand people live in the agglomeration, mostly professing Orthodoxy and Islam.
- Pervouralsk. Another large city in the Sverdlovsk region with a population of about 120,000. Founded in 1732, initially and until the revolution of 1917 it was a village, but in 1933 it acquired the status of a city. Local residents live quite densely per 1 sq. km – 1829, 97 people. If we compare the number of residents now and the number of people living in the territory of Pervouralsk at the time of its founding, we can talk about a more than thirty-fold increase. In 1735, only 400 people lived in the village, but in 1926 already 9,000 lived here, in 1939 - 44,000, and in 1962 already more than 100,000. The maximum number of residents was recorded in 1991, 1992 and 1993. – 144,000 people, but in 1995 there were already 8 thousand fewer people living in Pervouralsk. There is a persistent deterioration in the demographic situation, even though the city continues to be a major transport, industrial, commercial and cultural center.
Also large in the Sverdlovsk region are Verkhnyaya Pyshma, Krasnoturinsk, Polevskoy, Serov, Lesnoy, Asbest and Berezovsky.
Novouralsk
There is a fairly large settlement on the list of closed cities in the Sverdlovsk region - Novouralsk. It is home to about 81.5 thousand inhabitants.
The city was formed in 1941 after a light alloy plant began to be built in the vicinity of the modern settlement. In 1954, Novouralsk received city status. Remains one of 40 closed cities in Russia and one of ten owned by Rosatom.
The largest enterprises are the Ural Electrochemical Plant and the Novouralsk Instrument Plant. In recent years, the construction of multi-storey comfortable residential buildings has been actively developing in the city. It is noteworthy that most construction sites are located directly in the very center of the city. In addition, it is one of the largest energy centers located in the Northern Urals. Agriculture plays a significant role in the local economy.
Story
The Sverdlovsk region became a subject of the Russian Federation relatively recently. But this territory was inhabited in ancient times. Archaeologists have found multiple sites of ancient man, indicating that the first people lived in these lands back in the Paleolithic era, as well as the Iron Age.
In 1780 and 1796, two provinces were formed - Tobolsk and Perm and 6 counties were allocated. As a separate administrative unit, the Sverdlovsk region was formed after its separation from the Ural region in 1934. In 1938, another division was made, as a result of which the territory received an almost modern appearance. During the Second World War, more than 200 enterprises were evacuated to the Sverdlovsk region and continued their work here. During the Soviet era, the country's largest metallurgical, pipe and copper smelting plants were built here. The construction of these major giants contributed to the influx of workers.
Serov
The city of Serov, Sverdlovsk region, is considered an important transport hub for the region, where many railway, road, and pipeline transport lines intersect. Almost 98 thousand people currently live in the city.
It was founded relatively recently, even by the standards of the young Sverdlovsk region. The first settlement appeared here in 1894. The city was built around a new metallurgical plant with a full production cycle. Serov received city status in 1919.
Local industrial giants are the metallurgical plant, which bears the name of Serov, the ferroalloy plant and the Serov Mechanical Plant.
Marriages and divorces
The number of marriages is noticeably decreasing when compared with the second quarter of the last century and the number of divorces is increasing. Thus, in 1955 there were 12.4 marriages per 1000 inhabitants, in 1980 – 10.6 marriages, and in 2022 – 6.4 marriages. The percentage of divorces in the same 1955 was 0.9, and in 2022 it is 4.4; out of 6.4 marriages, more than half break up. In 2022, the situation has not improved, the indicators are approximately the same.
Ekaterinburg is a metropolis and an industrial center of global importance
Yekaterinburg is the recognized capital of the Urals, the largest city in the region and the region, with an area of 468 km². It occupies fourth place in the list of the largest cities in Russia, second only to two capitals and Novosibirsk. Its urban agglomeration, which is also one of the three most successfully developing post-industrial ones, occupies the same position in the all-Russian ranking of the largest. In the capital of the region there are such important organizations as:
- Administration of the Urals Federal District;
- 35 authorities of various territorial affiliations;
- Presidium of the regional branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences;
- headquarters unit of the Central Military District.
Ekaterinburg plays a vital role not only in the Russian but also in the world economy; it is included in the ranking of 600 most important cities on the planet from an economic point of view, accounting for 60% of the global gross domestic product. Leading industry segments include:
- metallurgy;
- metal processing;
- military industrial complex;
- heavy engineering;
- chemical industry;
- food production;
- light industry;
- creation of optical, electronic and electrical equipment;
- printing;
- instrumentation and others.
There are about 220 significant enterprises in the city, most of which are engaged in the manufacturing industry. In second place in terms of contribution to the economy are retail trade enterprises, of which more than 4,000 are registered. In the capital of the Urals, there is Koltsovo Airport, and a branch of the Trans-Siberian Railway passes through the city. Public transport is well developed here: in addition to buses and minibuses, there are metro, trams and trolleybuses. In addition, the regional center is included in the list of ten Russian cities with the largest vehicle fleet. Such a developed transport infrastructure and industry cause serious harm to the environment. In terms of air pollution, Yekaterinburg is included in the all-Russian anti-rating. Despite the abundance of manufacturing enterprises, exhaust gases cause the greatest harm: they account for more than 90% of harmful emissions.
Yekaterinburg has given the world many talented and famous people. Among the most famous natives is Boris Yeltsin; one of the most visited city attractions, the Yeltsin Center, is also associated with his name. Also from here are the storyteller Bazhov, singer Yuri Gulyaev, and the legendary rock groups Nautilus, Chaif and Agatha Christie. The local theaters are considered one of the best, and museums present a variety of exhibitions: from the history of literature to an amazing collection of minerals.
National composition
The predominant nation is Russians. Also in the Sverdlovsk region live many Tatars, Ukrainians, Bashkirs, Mari and Germans, there are Udmurts, Mordovians, Chuvashs and representatives of other small nations. People from Belarus and Azerbaijan have settled here long ago and firmly. Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and even China.
A certain proportion of the population consists of Moldovans, Jews, Roma, Georgians, Poles and Greeks. The Bashkirs, who have lived on these lands since ancient times, are considered the indigenous people.
Kachkanar is large in area, but not in numbers
Kachkanar ranks fourth in area - 317 km², and fifteenth in number of inhabitants - 38,996 people. Like many others in the region, it arose in the 19th century thanks to the wealth of the Ural mineral resources: platinum and gold were discovered nearby.
This led to the emergence of many mining settlements. On the basis of one of them, in the fifties of the last century, a village appeared, created for workers of the Kachkanar group of iron ore deposits. The formation of the Kachkanarsky mining and processing plant occurred during the same period: the enterprise, declared an all-Union construction site, today acts as a city-forming enterprise. Kachkanar gives the impression of a well-groomed, clean and green town. Most of the attractions are monuments and memorials, including those to the Liquidators of Nuclear Disasters, as well as the heroes of the Second World War and the Afghan War. Some of the most beautiful buildings are the Old and New Temples of the “Seeking the Lost” icon.
Forecast
In general, the forecast for improving the demographic situation and population growth is not very favorable; fewer people are still born than die or leave the region. The population decline is significantly influenced by the unfavorable economic situation in the world, environmental problems, difficulties with local employment, and the desire of young people to study in the capital.
The Sverdlovsk region is one of the largest in terms of population, almost 1.5 million people live in Yekaterinburg alone, but still this region is experiencing demographic problems common to all of Russia.
Ekaterinburg
(Sverdlovsk region)
OKATO code:
65401
Founded:
1723
City since:
1796 City of regional subordination
Center:
Sverdlovsk region
Urban areas, population as of 01/1/2021
| Verkh-Isetsky | Leninist | Chkalovsky |
| Railway | October | |
| Kirovsky | Ordzhonikidzevsky |
| The city was formerly called: | ||
| Ekaterinburg | 1924 | |
| Sverdlovsk | 1924 | 1991 |
| Telephone code (reference phone) | |
| 343******* | — |
Deviation from Moscow time, hours:
2
Geographic latitude:
56°50′
Geographic longitude:
60°35′
Altitude above sea level, meters:
260 Sunrise and sunset times of the Sun and Moon in the city of Yekaterinburg
Ufa
- Population: 1,124,226 people (2019)
- Founded 1574
The capital of Bashkortostan, the largest oil refining center in Russia, an important transport hub. Multi-faith religious center.
The millionaire city of Ufa is the most spacious in the Russian Federation; in 2010, there were 698 m² of urban territory per resident.
In 2015, Ufa is scheduled to host the BRICS and Shanghai Cooperation Organization summits.
Ufa took 2nd place in terms of living comfort according to the integral rating of the 100 largest cities in Russia in 2012; and 2nd place according to the Forbes rating “The best cities in Russia for business - 2012”.
The city lies on the Pribelsky ridge-undulating plain, 100 km west of the ridges of the Southern Urals, on the banks of the river. Belaya, with the river flowing into it. Dema and Ufa. Mainly located on the Ufimsky Peninsula, between the Belaya and Ufa rivers. The city is 53 km long - from north to south, 28 km - from west to east.
Ufa is the 3rd longest city in the Russian Federation (Sochi and Volgograd).