Current data
The number of inhabitants is 2,196,000 inhabitants. In the cities of Primorye, the environment is not good. The plight is associated with companies that handle and transport coal in large quantities. A large anthropogenic load falls on the shoulders of residents. Transshipment of coal is carried out in an open way, but the situation is changing, the regulatory authorities have taken up the solution. Now government agencies are forcing companies to build protective devices and special structures to improve the disposal of industrial waste. The number of inhabitants in the territory in 2008 was 1,789,234.
The industrial industry of the Primorsky region does not lag behind in development. More than a hundred manufacturing plants operate at full capacity in the city.
- Askold - the plant produces high-quality pipeline fittings
- Spasskcement produces cement and clinker.
- The shipyard carries out repairs of ships of all models.
- has been operating since 2016, selling construction materials.
- Primorsky Plant is a large ship repair company. The company services 80-100 ships and boats annually.
- The Pacific Fleet Rope carries out repair work on ships of the naval forces of the FSB ocean fleet.
- PJSC is a company engaged in the production of steam power protection control systems.
Brown coal deposits have been found on the territory of Primorye. In 1932, mines were designed and a powerful hydroelectric power station was built.
Hunting in Primorsky Krai
Here they hunt elk, wapiti, wild boar, roe deer, sika deer, brown bear; of small animals - brown hare, white hare, Manchurian hare, badger, fox; from field game - pheasant; from waterfowl - geese, ducks and waders. In addition, there is commercial hunting for fur-bearing animals - wolf, sable, squirrel, mink, otter, raccoon dog and muskrat.
The greatest interest is in hunting for male red deer during the roar and on salt licks. The most productive lands are located in Chuguevsky, Olginsky, Krasnoarmeysky, Terneysky and Pozharsky districts. Hunting for roe deer opens only in the autumn-winter period.
The greatest interest is in hunting for male red deer during the roar and on salt licks.
In addition, the largest subspecies of wild boar lives in the Primorsky Territory. Approach hunting is often done in feeding areas, as well as very exciting hunting with dogs. Wild boar habitats: Anuchinsky, Partizansky, Lazovsky, Olginsky, Chuguevsky, Krasnoarmeysky and Pozharsky districts.
Sika deer are searched for in the Khasansky, Nadezhdinsky, Ussuriysky and Shkotovsky districts. The elk lives only in remote and hard-to-reach places in the Krasnoarmeysky, Pozharsky and Terneysky districts.
The brown bear's habitat includes the territories of Anuchinsky, Chuguevsky, Olginsky, Dalnerechensky, Krasnoarmeysky, Terneysky and Pozharsky districts. Of the traditional types of bear hunting, hunting from the approach and in dens is considered the most successful.
Waterfowl hunting is open for only 10 days in the spring and for 2 months in the fall. Pheasant hunting - in the fall for 20 days.
Statistics by year
Due to current trends, the statistics of people living in the territory of the Primorsky Territory is decreasing; in 2014, the number of people living in the region was 1941.6, in 2017 -1917.3, in 2022 it is predicted to be 1886.5. The picture presented is grim, with population decline occurring every year.
This phenomenon is associated with the remoteness of the object from the center, the high cost of moving, and the climatic features of the Primorsky Territory. Japanese citizens are gradually migrating to areas where they develop businesses and get jobs, but Russians still make up the bulk of the ethnic composition. The number of people in a city depends on the birth rate and population migration.
Medium-sized cities 20-100 thousand people
Arsenyev
Population 52,471 (2018).
Spassk-Dalniy
Population 40,717 people (2018).
Big Stone
Population 38,042 people (2018). The city is home to Dalnevostochny, which in the short term will be the largest shipbuilding enterprise in the country.
Partizansk
Population 37,470 people (2016).
Lesozavodsk
Population 37,059 (2018).
Dalnegorsk
Population 34,694 people (2018).
Dalnerechensk
Population 25,786 people (2018).
Fokino (Primorsky Krai)
There are other settlements and objects with this name, see Fokino
Population 23,077 people (2018). It should not be confused with the city of the same name in the Bryansk region. Closed city of the Pacific Fleet.
List of cities
Large agglomerates: Nakhodka and Vladivostok. The structure includes provincial points: Bolshoy Kamen, Artem, Dalnerechensk, Akhtarsk, Partizansk, Fokino, Spasik-Dalniy, Ussuriysk, Lesozavodsk, Dalnegorsk.
Arseniy forms the Arseninsky urban district. Founded in 1902 as the village of Semenovka, which united several points. The city has had an aviation service since war times. For 70 years it has been producing combat aircraft K52-navigator and K-50-black shark. Number of employees: 62,00 employees.
The population of Akhtarsk is 32,349 people. Elderly people live in a provincial facility, the required number of jobs is not provided, and there are no comfortable conditions. The infrastructure and economy of Akhtarsk are poorly developed; on the territory of the facility there is a kindergarten, a school, several shops, a clinic, a hospital. Akhtarsk, remote from the center, is experiencing budgetary difficulties that are difficult for the local administration to solve without the help of the ministry.
Dalnorechensk population 28,482 people. The point was developed by the Cossacks and named the village of Grafskaya, in honor of N. N. Muravyov. Since 1897 it was called Iman in Chinese, but after 1972 as a result of the Chinese conflict, it was renamed Dalnorechensky. The province is located on the banks of the Malinovka and Ussuri rivers. 3 km before Dalnorechensk there are three extinct volcanoes of the Salskaya Sopka. To get to the center of the capital you need to travel 400 km. Logistics. Transport services are minibuses, buses and taxis. On clear days, from almost anywhere in the city you can see the outlines of mountain ranges - the spurs of the Sikhote-Alin. Yes, and don’t forget about the taiga: the diversity of flora and fauna, rivers and lakes.
In total there are 12 cities and 26 rural areas. Artem has a population of 106,440 citizens and is located along the Knevichanka River. The name of the reservoir is of semi-Japanese origin. In the 1920s, before the Japanese War, people with Japanese cultural heritage lived on the territory of the city of Artem.
CITIES OF PRIMORSKY REGION
Primorsky Territory total population - 2022.5 men - 970.3 women - 1049.2 Vladivostok1) total population - 610.2 men - 285.4 women - 324.8 Artem 1) total population - 111.6 men - 52.7 women - 58.9 Nakhodka 1) total population - 172.7 men - 83.8 women - 88.9 Ussuriysk total population - 154.8 men - 74.6 women - 80.2 Population density (as of January 1, 2006), people per 1 km2: Primorsky Territory - 12.3 Vladivostok - 1086.7 Artem - 220.4 Nakhodka - 529.9 Ussuriysk - 895.3 |
Districts - 24 Cities - 12 Urban districts (districts) - 5 Urban settlements - 31 Rural administrations (including village councils, volosts, rural districts and local governments) - 226 Cities (number of inhabitants - estimate as of January 1, 2006, thousand people): Vladivostok - 583.7 Nakhodka - 171.7 Ussuriysk - 154.8 Artem - 102.3 Arsenyev - 59.7 Spassk-Dalniy - 46.9 Partizansk - 41.6 Lesozavodsk - 42.0 Dalnegorsk - 39.2 Bolshoi Kamen - 38.2 Dalnerechensk - 29.1 Fokino - 25.8 Territory area, thousand km2: Primorsky Krai - 164.7 Vladivostok 1) - 561.5 Artem 1) - 506.4 Nakhodka 1) - 325.9 Ussuriysk - 172.9 |
__________ 1) Including settlements subordinate to the city administration.
GROUPING CITIES BY PERMANENT POPULATION1)
| Total | including the number of inhabitants, thousand people | ||||||||||
| until 3 | 3 — 4,9 | 5 — 9,9 | 10 -19,9 | 20 — 49,9 | 50 — 99,9 | 100 — 249,9 | 250 — 499,9 | 500 — 999,9 | 1 million or more | ||
| Number of cities | |||||||||||
| 2005 | 12 | — | — | — | — | 7 | 1 | 3 | — | 1 | — |
| 2006 | 12 | — | — | — | — | 7 | 1 | 3 | — | 1 | — |
| Population, thousand people | |||||||||||
| 2005 | 1344,7 | — | — | — | — | 265,6 | 60,6 | 431,7 | — | 586,8 | — |
| 2006 | 1335,0 | — | — | — | — | 262,8 | 59,7 | 428,8 | — | 583,7 | — |
| __________ 1) Estimate as of January 1. | |||||||||||
DISTRIBUTION OF POPULATION OF VLADIVOSTOK AND CITIES WITH A POPULATION OVER 100 thousand people BY AGE GROUPS1) (thousand people)
| Vladivostok | Artem | Nakhodka | Ussuriysk | |||||
| 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | |
| Whole population | 586,8 | 583,7 | 102,2 | 102,3 | 173,5 | 171,7 | 156,0 | 154,8 |
| including those aged: | ||||||||
| younger than able-bodied | 80,6 | 78,0 | 16,5 | 16,1 | 27,6 | 26,4 | 25,2 | 24,4 |
| of which children aged 1-6 years | 25,9 | 27,3 | 5,2 | 5,4 | 8,8 | 9,0 | 8,5 | 8,9 |
| able-bodied2) | 395,2 | 392,8 | 66,2 | 66,6 | 114,6 | 113,5 | 105,0 | 104,6 |
| older than able-bodied | 111,0 | 112,9 | 19,5 | 19,6 | 31,3 | 31,8 | 25,8 | 25,8 |
| __________ 1) Estimate as of January 1. 2) Men 16-59 years old, women 16-54 years old. | ||||||||
SHARE OF VLADIVOSTOK AND CITIES WITH A POPULATION OF OVER 100 thousand people IN THE MAIN SOCIO-ECONOMIC INDICATORS OF PRIMORSKY TERRITORY in 2005 (percent)
| Vladivostok1) | Artem1) | Nakhodka1) | Ussuriysk | |
| Population (est. January 1, 2006) | 30,2 | 5,5 | 8,6 | 7,7 |
| Average annual number of employees in organizations | 39,2 | 3,9 | 9,2 | 9,1 |
| Availability of fixed assets of organizations2) (at the end of the year) | 53,0 | 1,6 | 5,3 | 8,1 |
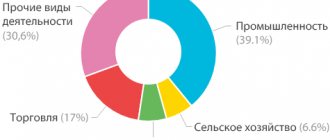
| Volume of shipped goods of own production, work and services performed in-house, by type of activity 3): | ||||
| mining | 2,1 | 2,8 | 0,2 | 0,1 |
| manufacturing industries | 33,4 | 2,8 | 12,1 | 14,7 |
| production and distribution of electricity, gas and water | 31,6 | 15,5 | 4,4 | 4,0 |
| Scope of work performed for the type of activity “Construction” | 44,6 | 4,3 | 14,5 | 14,1 |
| Commissioning of the total area of residential buildings | 50,3 | 7,8 | 12,2 | 11,6 |
| Retail trade turnover | 53,4 | 3,5 | 8,7 | 9,8 |
| Investments in fixed capital | 45,5 | 3,8 | 10,2 | 5,5 |
| __________ 1) Including settlements subordinate to the city administration. 2) At the full accounting value of large and medium-sized commercial and non-profit organizations. 3) For large and medium-sized organizations. | ||||
SOCIO-ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF VLADIVOSTOK AND CITIES WITH A POPULATION OF OVER 100 THOUSAND PEOPLE
| Vladivostok1) | Artem1) | Nakhodka1) | Ussuriysk | |||||
| 2004 | 2005 | 2004 | 2005 | 2004 | 2005 | 2004 | 2005 | |
| POPULATION | ||||||||
| Population (end of year estimate), thousand people | 613,4 | 610,2 | 111,5 | 111,6 | 174,6 | 172,7 | 156,0 | 154,8 |
| Number of births per 1000 population | 9,3 | 9,2 | 10,2 | 10,7 | 9,7 | 9,2 | 11,6 | 11,0 |
| Number of deaths per 1000 population | 13,4 | 13,0 | 18,9 | 19,0 | 14,0 | 14,6 | 16,9 | 17,5 |
| Natural increase, decrease (-) per 1000 population | -4,1 | -3,8 | -8,7 | -8,3 | -4,3 | -5,4 | -5,3 | -6,5 |
| WORK | ||||||||
| Average annual number of employees in organizations, thousand people | 272,6 | 254,7 | 27,4 | 25,6 | 63,7 | 59,6 | 63,5 | 58,9 |
| Number of unemployed citizens registered with the state employment service (at the end of the year), people | 4452 | 5158 | 1233 | 1063 | 1557 | 2069 | 14412) | 22122) |
| of them are recognized as unemployed | 3610 | 3824 | 1076 | 953 | 1393 | 1915 | 13622) | 14642) |
| LIVING STANDARD OF THE POPULATION AND SOCIAL SPHERE | ||||||||
| Average monthly nominal accrued wages, rub. | 7933,1 | 10267,0 | 6768,0 | 8446,4 | 8049,3 | 10070,3 | 6887,0 | 8571,7 |
| Average amount of assigned monthly pensions (at the end of the year), rub. | 2142,1 | 2721,9 | 2033,9 | 2523,5 | 2049,0 | 2542,7 | 2018,42) | 2510,02) |
| Number of pensioners (at the end of the year), thousand people | 138,4 | 139,7 | 28,2 | 28,2 | 38,3 | 38,7 | 42,12) | 42,32) |
| Total area of residential premises per average city resident (at the end of the year), m2 | 18,7 | 19,0 | 19,2 | 19,3 | 17,1 | 17,4 | 18,5 | 18,8 |
| Number of preschool institutions | 117 | 117 | 24 | 24 | 35 | 34 | 31 | 31 |
| in them: | ||||||||
| children, thousand people | 16,0 | 16,3 | 3,0 | 3,2 | 5,6 | 5,8 | 4,6 | 4,8 |
| places, thousand | 16,0 | 15,7 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 5,4 | 5,4 | 3,9 | 4,0 |
| Enrollment of children in preschool educational institutions (at the end of the year), as a percentage of the number of children of the corresponding age | 59,7 | 56,4 | 52,6 | 53,8 | 65,7 | 63,7 | 55,4 | 53,0 |
| Number of daytime educational institutions (at the beginning of the school year) | 115 | 117 | 28 | 28 | 39 | 38 | 30 | 29 |
| Number of students in daytime general education institutions, thousand people | 61,2 | 58,1 | 12,5 | 11,9 | 19,8 | 18,2 | 16,8 | 15,9 |
| Number of doctors, people: | ||||||||
| Total | 6147 | 6294 | 409 | 382 | 823 | 813 | 669 | 702 |
| per 10,000 population | 100,2 | 103,1 | 36,7 | 34,2 | 47,1 | 47,1 | 42,9 | 45,4 |
| Number of nursing staff, people: | ||||||||
| Total | 5786 | 5749 | 546 | 539 | 1444 | 1492 | 1672 | 1757 |
| per 10,000 population | 94,3 | 94,2 | 49,0 | 48,3 | 82,7 | 86,4 | 107,2 | 113,5 |
| Number of hospitals | 39 | 38 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
| Number of hospital beds: | ||||||||
| total, thousand | 8,2 | 8,1 | 0,6 | 0,6 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 1,8 | 1,8 |
| per 10,000 population | 133,7 | 133,5 | 53,6 | 53,6 | 88,4 | 87,7 | 114,4 | 113,7 |
| Number of medical outpatient clinics | 159 | 171 | 19 | 19 | 36 | 51 | 27 | 38 |
| Capacity of medical outpatient clinics, visits per shift: | ||||||||
| total, thousand | 13,8 | 14,3 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 4,0 | 4,4 | 2,9 | 3,4 |
| per 10,000 population | 225,1 | 233,7 | 167,6 | 167,3 | 231,3 | 257,6 | 186,6 | 216,8 |
| Number of registered crimes | 17083 | 23100 | 2457 | 3416 | 4144 | 5855 | 55872) | 61782) |
| Persons who committed crimes were identified, people | 5047 | 4811 | 1061 | 1049 | 1558 | 1557 | 18432) | 17952) |
| ENTERPRISES AND ORGANIZATIONS | ||||||||
| Number of enterprises and organizations (at the end of the year; according to state registration) | 33827 | 37089 | 1940 | 2035 | 5010 | 5399 | 2744 | 2925 |
| MINERAL MINING, MANUFACTURING, PRODUCTION AND DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRICITY, GAS AND WATER3) | ||||||||
| Number of operating organizations by type of activity (at the end of the year): | ||||||||
| mining | … | 3 | … | 3 | … | 2 | … | 3 |
| manufacturing industries | … | 239 | … | 43 | … | 75 | … | 92 |
| production and distribution of electricity, gas and water | … | 52 | … | 7 | … | 27 | … | 26 |
| Volume of shipped goods of own production, work and services performed in-house, by type of activity, million rubles: | ||||||||
| mining | 126,3 | 133,9 | 153,6 | 180,4 | 13,4 | 11,8 | 2,7 | 4,1 |
| manufacturing industries | 8325,6 | 9514,5 | 695,3 | 791,7 | 2257,0 | 3444,6 | 3675,1 | 4189,1 |
| production and distribution of electricity, gas and water | 6468,9 | 8101,9 | 3054,9 | 3980,2 | 930,7 | 1127,6 | 515,2 | 1023,1 |
| CONSTRUCTION | ||||||||
| Amount of work performed by type of activity “Construction”, million rubles. | 5143,7 | 6271,0 | 475,1 | 606,4 | 1725,3 | 2038,4 | 1587,2 | 1982,8 |
| Commissioning of social and cultural facilities using all sources of funding: | ||||||||
| residential buildings, thousand m2 of total area | 116,9 | 124,2 | 7,5 | 19,2 | 16,3 | 30,1 | 19,0 | 28,6 |
| apartments (including apartments in dormitories) | 1285 | 1428 | 69 | 213 | 135 | 369 | 243 | 411 |
| preschool institutions, places | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| educational institutions, student places | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| hospital facilities, beds | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| outpatient clinics, visits per shift | — | — | — | — | 350 | — | — | — |
| PASSENGER TRANSPORT AND COMMUNICATIONS | ||||||||
| Number of routes: | ||||||||
| buses (in intracity traffic)4) | 28 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 16 | 26 | 16 |
| trams | 4 | 4 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| trolleybuses | 6 | 6 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Number of passengers transported per year, million people: | ||||||||
| by bus (in intracity traffic)4) | 11,2 | 8,3 | 1,4 | 1,1 | 3,8 | 7,8 | 10,5 | 7,4 |
| by trams | 33,9 | 25,3 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| trolleybuses | 22,7 | 17,7 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Number of telephone sets of the city public telephone network, thousand units. | 234,6 | 247,3 | 19,6 | 22,4 | 53,1 | 55,8 | 41,8 | 44,2 |
| including apartments | 184,3 | 194,5 | 16,5 | 19,0 | 43,7 | 45,9 | 35,9 | 37,0 |
| Number of payphones of the city telephone network (including universal ones), pcs. | 2193 | 1567 | 54 | 57 | 241 | 170 | 296 | 300 |
| TRADE AND SERVICES TO THE PUBLIC | ||||||||
| Retail trade turnover (in actual prices): | ||||||||
| total, million rubles | 34610,9 | 44881,7 | 2387,4 | 2971,0 | 5807,1 | 7319,7 | 5327,8 | 8206,4 |
| per capita, rub. | 56272 | 73360 | 21420 | 26627 | 33095 | 42155 | 34031 | 52811 |
| Index of physical volume of retail trade turnover, as a percentage of the previous year | 119 | 119 | 106 | 114 | 114 | 115 | 116 | 141 |
| Public catering turnover (in actual prices), million rubles. | 1543,7 | 1930,4 | 126,3 | 203,1 | 253,9 | 259,7 | 221,3 | 373,0 |
| Index of physical volume of public catering turnover, as a percentage of the previous year | 101,6 | 102,9 | 112 | 132,4 | 141 | 84,2 | 131 | 138,8 |
| Number of stores, pavilions5) (at the end of the year) | 177 | 159 | 34 | 45 | 23 | 58 | 77 | 93 |
| their retail area, m2 | 31720 | 34406,1 | 3747 | 6022,2 | 3951 | 7883 | 10957 | 11589,1 |
| Volume of paid services to the population (in actual prices): | ||||||||
| total, million rubles | 16112,9 | 19910,5 | 1065,3 | 1333,7 | 2713,0 | 3465,5 | 2076,8 | 2857,1 |
| per capita, rub. | 26195,6 | 32543,9 | 9553,9 | 11952,5 | 15459 | 19958,3 | 13262 | 18386,4 |
| Volume of household services to the population (in actual prices): | ||||||||
| total, million rubles | 1380,1 | 1539,3 | 89,1 | 100,9 | 308,0 | 350,1 | 227,1 | 257,7 |
| per capita, rub. | 2243,7 | 2516,0 | 798,9 | 904,3 | 1754,8 | 2016,0 | 1450,4 | 1658,4 |
| INVESTMENTS | ||||||||
| Investments in fixed assets (in actual prices), million rubles. | 7893,6 | 10019,6 | 766,2 | 828,4 | 1830,0 | 2246,9 | 739,0 | 1207,5 |
| Share of investments in fixed assets financed from budgetary funds in the total volume of investments4), percent | 30,5 | 28,7 | 7,9 | 16,0 | 9,6 | 2,9 | 23,0 | 31,4 |
| including at the expense of the federal budget | 18,2 | 18,6 | 5,1 | 10,9 | 2,9 | 1,2 | 10,4 | 3,6 |
| __________ 1) Including settlements subordinate to the city administration. 2) Including the Ussuriysk region. 3) For large and medium-sized organizations. For 2005, data is provided on the number of operating organizations and territorially separate divisions. 4) Without small businesses. 5) For trade and public catering organizations (excluding small businesses). | ||||||||
Regions of Russia. Main socio-economic indicators of cities - 2006. Copyright © Federal State Statistics Service
Age and sex composition
The population of the Primorsky Territory is 1,895,868 people, of which 174,060 are men, 165,050 are women, and 339,110 are children. Information collected from official information as of January 1, 2020. Women of working age (over 55) are equal to - 1099785. A separate category, city statistics - men - 131872, women - 124677, children - 256549. Rural density of the Primorsky Territory: men - 42188, women - 40373.
Administrative-territorial structure
According to the Law “On the administrative-territorial structure of the Primorsky Territory
"and the Register of administrative-territorial and populated localities of the Primorsky Territory, the subject of the Russian Federation includes the following administrative-territorial units:
- 12 cities of regional subordination, 5 intra-city districts (Vladivostok districts: Leninsky, Pervomaisky, Pervorechensky, Sovetsky, Frunzensky);
The administrative center of the region is the city of Vladivostok.
Natural increase
Natural increase allows you to find out the percentage of increase in the birth rate that prevails over the number of deaths. In 2018, the natural increase is 5665, in 2022 -7529, which indicates an increase in the decline in the share of citizens. For example, in 2022 the number of deaths exceeded the number of births by 7498, that is, the number of citizens of the region decreased by 6.8 thousand inhabitants. In 2022, the number of deaths became equal to 2701.
The increase in migration did not affect the restoration of the demographic situation in the region, since only 600 people arrived in Primorye. Referring to current information from 1.01. In 2020, 1,895,900 people lived in the territory of the Primorsky Territory. In 2019, there were 1,902,700 residents, 18.2 thousand were born, and 25,000 died. From 2022 to 22020, the region lost more than 13,000 people of the stronger sex.
Guides in Primorsky Krai
All guides in Primorsky Krai
Excursions by Konstantin Grigorets
- Nakhodka, Triozerye, Ezhovaya on an SUV
- By SUV to the Gamow Peninsula
- Cape Tobizin and Russky Island by SUV
All 4 excursions
Excursions by Mikhail Simanchuk
- Travel to Shkota Island
- Gamow Peninsula - Far Eastern Marine Reserve
- Top 8 Instagram places in Vladivostok
All 5 excursions
Excursions of Irina Olegovna Demidenko
- Sightseeing tour of Vladivostok and the island. Russian
- Sightseeing tour "Evening Vladivostok"
- Kravtsovskie waterfalls and the Land of the Leopard national park
All 4 excursions
Excursions of Vladimir Vladimirovich Turkov
- Excursion to Primorsky Safari Park, Lazurnaya and Steklyannaya Bays from Vladivostok
- Sightseeing tour: Russky Island with a visit to the wild beach (snorkeling: mask, snorkel, fins)
- Voroshilov battery - past and present.
All 6 excursions
Excursions of Arthur Ilsurovich Romanenko
- Fort No. 4 of the Vladivostok fortress
- Russky Island: “Far Eastern Kronstadt”
- Fort No. 1 of the Vladivostok Fortress - full inspection
All 6 excursions
All guides in Primorsky Krai
Migration
Migration movement for 2022. In 2022, 34,000 residents arrived in the Primorsky Territory, almost 60% were Russians who arrived from abroad - 13,900. -33,400 left the Primorsky Territory, the flow coefficient is 0.7. 2022 was productive. The level of the number of visitors has exceeded the 2022 attendance threshold. From 2015 to 2018, the number of residents decreased by 15,000. Primorsky Krai always remains in first place in seafood production.
Forecast. According to young people and economic experts, the region is located far from the center and has no prospects for business development. Migration outflow occurs either gradually or abruptly. The influx of migrants comes from the shores of the Japanese islands. Residents from neighboring countries (Japan) are actively involved in fishing, trade, and scientific and technological research in the Primorsky Territory. The indigenous inhabitants of Primorye immigrate to remote regions of Russia; the climatic conditions and microclimate are not suitable for most residents.
Content
- 1 Largest cities 500 thousand - 1 million people 1.1 Vladivostok
- 2.1 Ussuriysk
- 3.1 Arsenyev
History of Ussuriysk
Founded by settlers from the Astrakhan and Voronezh provinces as the village of Nikolskoye on the territory of the once prosperous Bohai state. The construction of the Trans-Siberian Railway in 1891 and the transformation of Nikolsk into a large railway junction breathed new life into it. In 1898 a city called Nikolsk-Ussuriysky was formed. In 1935-1957 was called Voroshilov after the name of the Soviet party and military leader K. E. Voroshilov (1881-1969). Ussuriysk is the birthplace of the popular actor B. Khmelnitsky.